Ingest Tokens
Security Requirements and Controls
Change Ingest tokenspermission
Tokens are used to provide authentication for ingesting data into LogScale. An Ingest Token is a unique string that identifies a repository and allows you to send data to that repository.
Tokens are used in combination with the LogScale endpoint to ingest data. For more information on endpoints, see LogScale URLs and Endpoints.
You need to Generate a Repository Ingest Token and then use the token when configuring data ingestion to your repositories. See Third-Party Log Shippers or Ingest API for details on how tokens are used in different ingest methods.
Ingest tokens can only be used to ingest data; you cannot use them to query LogScale, log in, or read any data.
Note
For better security, as of 1.77 you can no longer list ingest tokens for system repositories using GraphQL. If you try to do so, the following message is returned: You don't have permission to read ingest tokens.
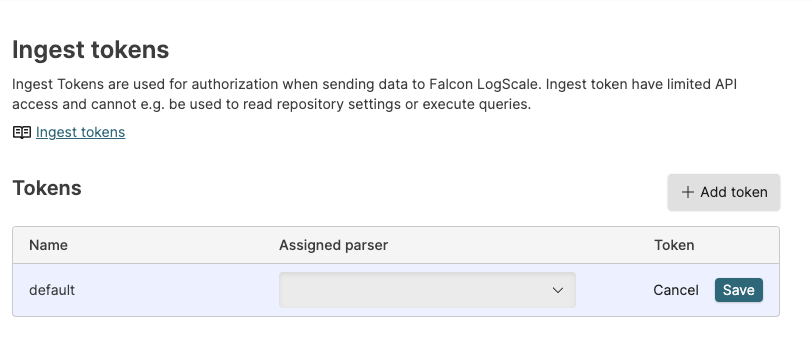 |
Figure 85. Ingest Tokens
Ingest tokens are tied to a repository, not a user. This provides a better way of managing access control and is more convenient for most use cases. For example, if a user leaves the organization or project, you do not need to re-provision all agents that send data with a new token. You also do not have to create fake user accounts.
Additionally, LogScale provides the possibility to generate Personal API Tokens which are user specific tokens that can be used for administration tasks. Personal API Tokens cannot be used to ingest data.
Tokens Supporting Ingest
LogScale supports different tokens to provide security across the cluster. Different tokens allow the ingestion of data, but how and where the data is ingested differs:
Repository Ingest Token
A Repository Ingest Token is associated with a specific repository and parser. When using this token, data can be ingested directly to the repository and the data will only be ingested to the associated repository.
To create a Repository Ingest Token, see Generate a Repository Ingest Token.
An Organization API Token can be used to ingest data into repositories when the token has the
Ingest across all repositories within organizationpermission. This allows for data to be ingested to a repository with the repository specification provided in the event data when using Ingesting with HTTP Event Collector (HEC). For more information, see Ingesting with HTTP Event Collector (HEC).System API Token
System API Tokens with the
Ingest across all repositories within clusterpermission can ingest into repositories using an the repository name in the event.
A comparison of the different tokens and capability are shown below:
| Token Type | Repository Target | Ingest to Multiple Repositories | Ingest to System Repositories | Ingest to Sandbox Repository |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Repository Ingest Token | Specific Repository | No | Yes | Yes |
Organization API Token (with
Ingest across all repositories within organization permission)
| Any (driven by event data or log shipper) | Yes | No | No |
System API Token (with Ingest across all repositories within cluster permission)
| Any (driven by event data or log shipper) | Yes | No | No |
Generating Ingest Tokens and Assigning Parsers
Security Requirements and Controls
Change Ingest tokenspermission
From the repository's page you can manage ingest tokens and assign a parser to a token. For more information on the actions you can perform from the repositories settings page, see Basic Information.
Generate a Repository Ingest Token
On the
Ingest tokenspage, click to add a token to this repository.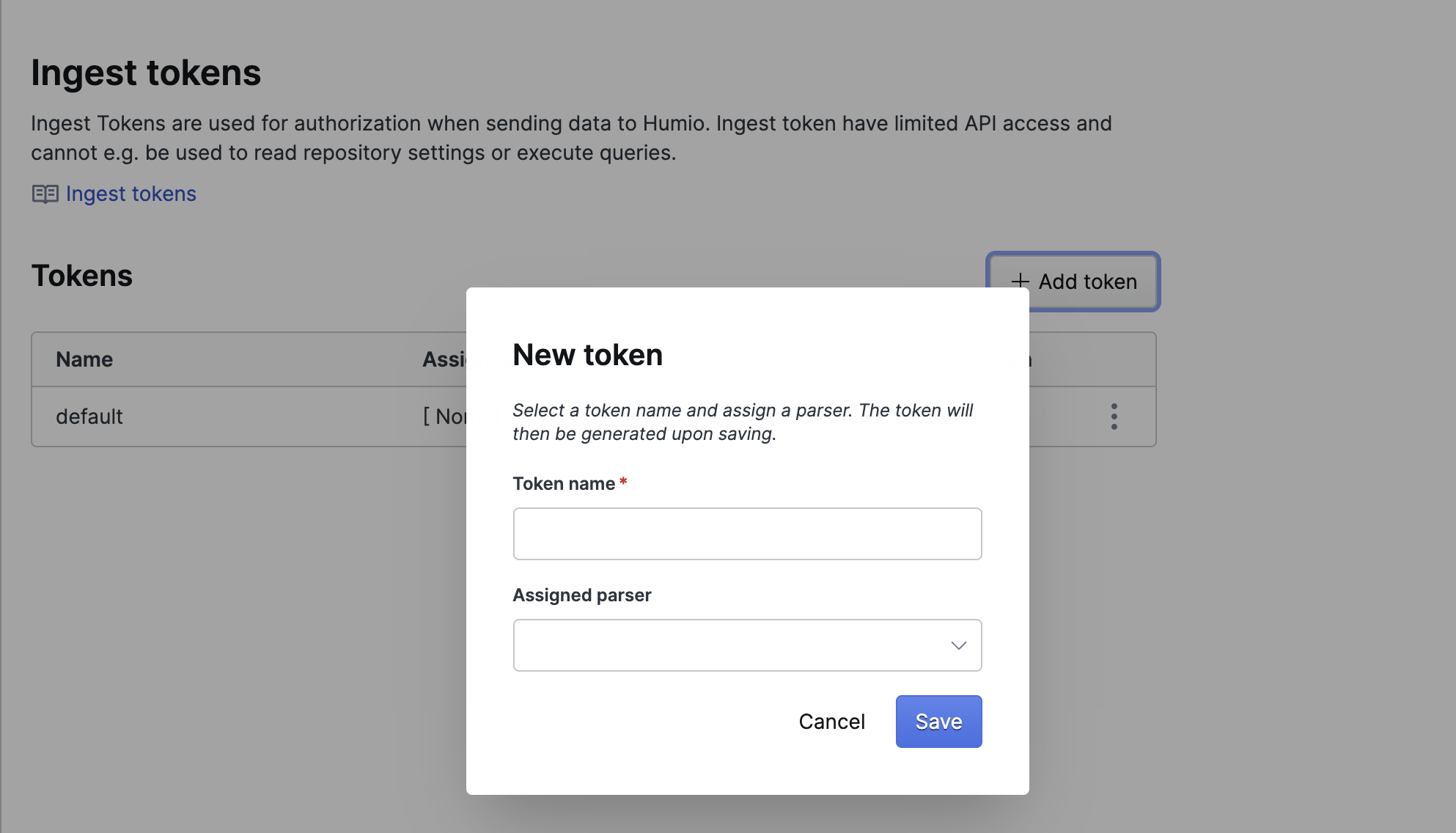
Figure 86. Generate Token
In the New token dialog box, enter a token name to identify the token. You may want to use this to identify the token you have assigned to a specific host, data source, log type or other identifier.
You can optionally set an Assigned Parser by selecting a parser from the list. For more information on parsers, see Parse Data.
Click .
To add a token with a custom application, use the addIngestTokenV3() mutation in the GraphQL API.
Assign a Parser to a Token
Security Requirements and Controls
Change Ingest tokenspermission
You can change the parser assigned to a token by editing a token.
Click the ⋮ icon next the token you want to edit and click . Editing the token allows you to change the assigned parser. For more information, see Assigning Parsers to Ingest Tokens.
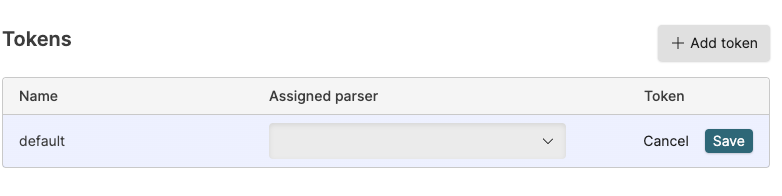
Figure 87. Editing an Existing Token
Click once you have made the required changes.
To assign a parser to an ingest token from a custom application, use the assignParserToIngestTokenV2() mutation field in the GraphQL API. You can use unassignIngestToken() to unassign a parser from an ingest token.
Delete an Ingest Token
Security Requirements and Controls
Change Ingest tokenspermission
You can delete a token but note that deleting the token will prevent any existing ingest processes using that token to ingest data to LogScale.
To delete a token from you own custom application, use the removeIngestToken() mutation field in the GraphQL API.
Custom Tokens
Security Requirements and Controls
Change Ingest tokenspermissionManage clusterpermissionManage customer organizationspermission
We highly recommend you use automatically generated tokens whenever possible, but custom ingest tokens can be useful in cases where you already have a token in use and want LogScale to accept it, or where the log shipper requires tokens in a format that is not compatible with the ones automatically generated by LogScale.
Generally, ingest tokens should be sufficiently complex such that they are not easy to guess. When creating custom ingest tokens, it is your responsibility to ensure this.
To use custom tokens, the feature "CustomTokens" must first be enabled. This can be done by making the following GraphQL mutation (see GraphQL API):
mutation {
enableFeature(feature: CustomIngestTokens)
}Once enabled, root users can then create custom tokens via the GraphQL API:
mutation {
addIngestTokenV3(
input: {
repositoryName: "sandbox"
name: "MyIngestToken"
parser: "kv"
customToken: "myCustomToken"
}
) {
name
token
}
}The response will indicate an error, or the token if one has successfully been created. For example:
{
"data": {
"addIngestTokenV3": {
"name": "MyIngestToken",
"token": "myToken"
}
}
}