Charting Log Levels
If you have logs that contain log levels like
INFO,
ERROR, and
WARN, it can be
interesting to visualize them over time.
Sample input data. Here is example log data for this scenario (from a parser that extracts a field called loglevel from each line):
2023-09-18T13:43:26.464+0000 [kafka-producer-network-thread | producer-3] WARN o.a.k.c.p.i.Sender 42 ...
2023-09-18T13:39:28.487+0000 [timer-thread-8] ERROR c.h.b.BucketStorageUploadLatencyJob$ 43 ...
2023-09-18T13:43:04.248+0000 [timer-thread-3] INFO c.h.u.TimerExecutor$ 41 ...Query. To create this time chart, use the following query:
timeChart(loglevel)
This will count the number of occurrences of events that have a field
called loglevel
and put them in a series in the time chart based on their value. Based
on the example data above this would create a time chart with three
series, INFO,
ERROR and
WARN.
By default the count() function is used to
calculate the value of each bucket, but you can easily plot other
values by specifying other functions in the
function property of the
timeChart() function. For instance, if we use the
avg() function on the field
time:
timeChart(loglevel, function=avg(time))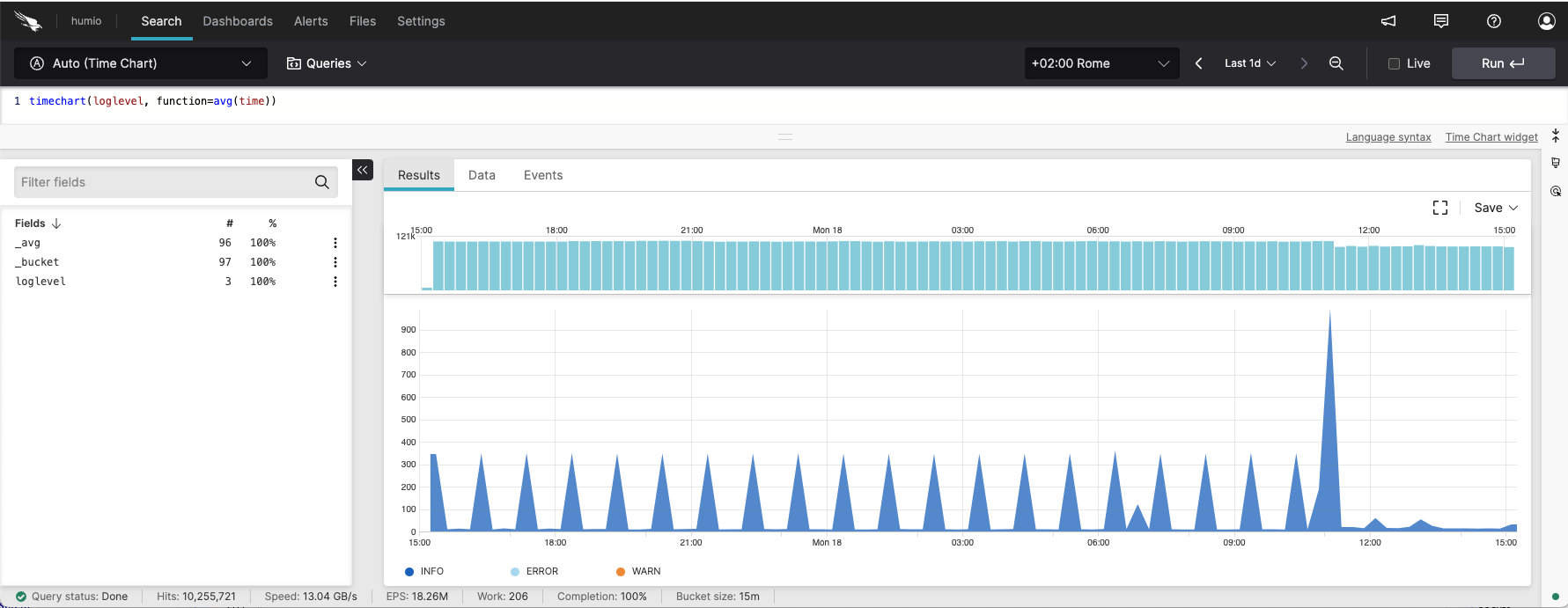 |
Figure 246. Timechart with Log Levels
We can see the average time that a database query takes. The
percentile() function is very useful as an
aggregate function in time charts when you wish to visualize response
times like this.