Repository and View Settings
Security Requirements and Controls
Change connections for a viewpermissionChange view or repo descriptionpermission
The Settings page of a repository or view
enables you to configure some key settings. The page is divided into a
number of sections:
General
Basic Information covers how to set the name of the repository, and other identity information.
Data Retention configure the data retention settings for the repository.
Field Aliasing shows the schemas configured for field aliasing in the repository.
Access Control
Permissions controls user access to the repository.
Data Connections
Connections define which repositories a view gets its data from.
Ingest
Ingest Tokens configure ingest tokens for ingesting and parsing data.
Block Ingest allows you to block the ingest of data.
Datasources control the data sources for a repository.
Tag Groupings control the tag groupings for a repository.
Listeners configure listeners for ingesting specific data types through integrations.
Egress
S3 Archiving configure archiving of ingested logs to Amazon S3
Event Forwarding forward events that are ingested into LogScale to other systems.
Other
Danger Zone enables changing the repository name or deleting the repository.
Packages
The creation, configuration and installation of Packages is described in the dedicated documentation, which you can find in Package Management for more information.
Note
The exact list of available options in this UI page will depend on the user permissions and repositories available. System repositories, for example, cannot be deleted and so the Danger Zone will not be shown. The personal Sandbox repository can't be deleted, and can't be configured with multiple users.
Basic Information
The tab, specifically the
section where you may
enter repository information in the
Basic Information
page. This description, along with the name of the repository, will
appear on the tab when you
first log into the LogScale Interface.
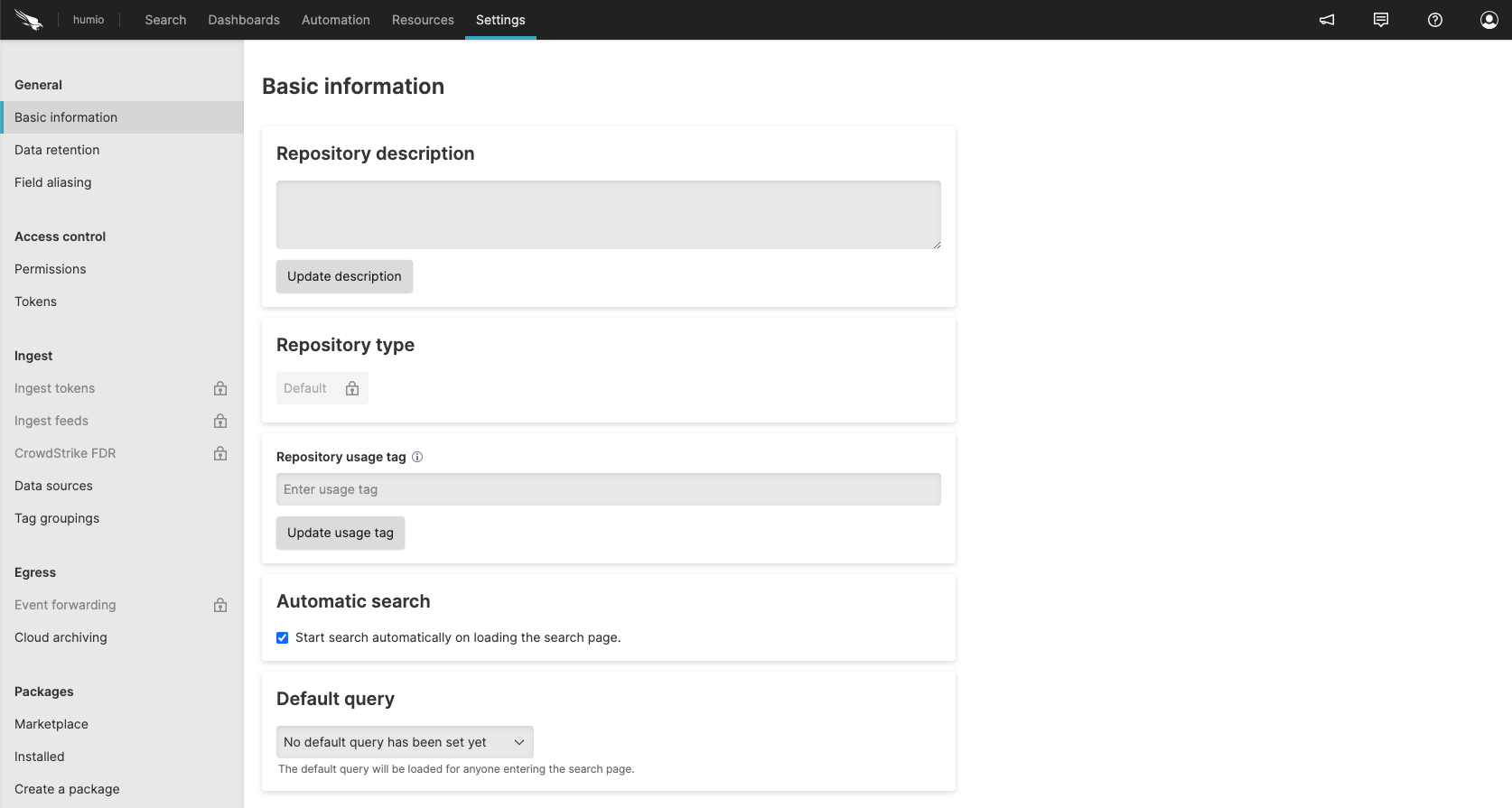 |
Figure 28. Basic Settings
Below is a list of each part of the Basic
Information panel, with descriptions of each:
Repository description
This is a description of the repository. To update it, type in the field and click .
Repository type
Use this to specify the type of repository. For example, you could select a trial or a managed repository (e.g., Falcon LTR).
Repository usage tag
This is where you may specify a tag for the repository so that it may be grouped with other repositories with the same tag. To set or update this, enter a tag and click .
Automatic search
Check this box if search should be started automatically when the Search page is loaded. Uncheck it if it you don't want it started automatically.
Default query
Related to the above about automatic search, you can set here the default query which is loaded by default when the search pages is loaded.
Data Retention
Security Requirements and Controls
Manage OrganizationspermissionManage clusterpermission
The Data retention
settings page shows how much data LogScale can store in a
repository and for how long. To free up space for new data, old data is
removed automatically when any of the following configured limits is
reached:
Ingest limit in GB (Uncompressed)
Automatically deletes old data when the ingest limit (raw data size) is reached. See LogScale Multiple-byte Units.
Storage size limit in GB (Uncompressed)
Automatically deletes old data when the stored data, including fields and data expanded or filters during parsing, is reached. See LogScale Multiple-byte Units.
Time limit in days
Automatically deletes old data when the event @timestamp passes beyond the configured limit.
Note
The
ManageClusterpermission allows Self-Hosted users to set the time retention above the specified limit.The maximum customer configurable limit within LogScale Cloud deployments is 365 days. Please Contact Support if you need to set a higher limit.
Field Aliasing
The Field aliasing
settings' page lists all the schemas configured for any field aliasing
being applied. For more information, see
Field Aliasing.
Permissions
Repository access can be configured on a per-user basis by adding a user and setting their role for each repository.
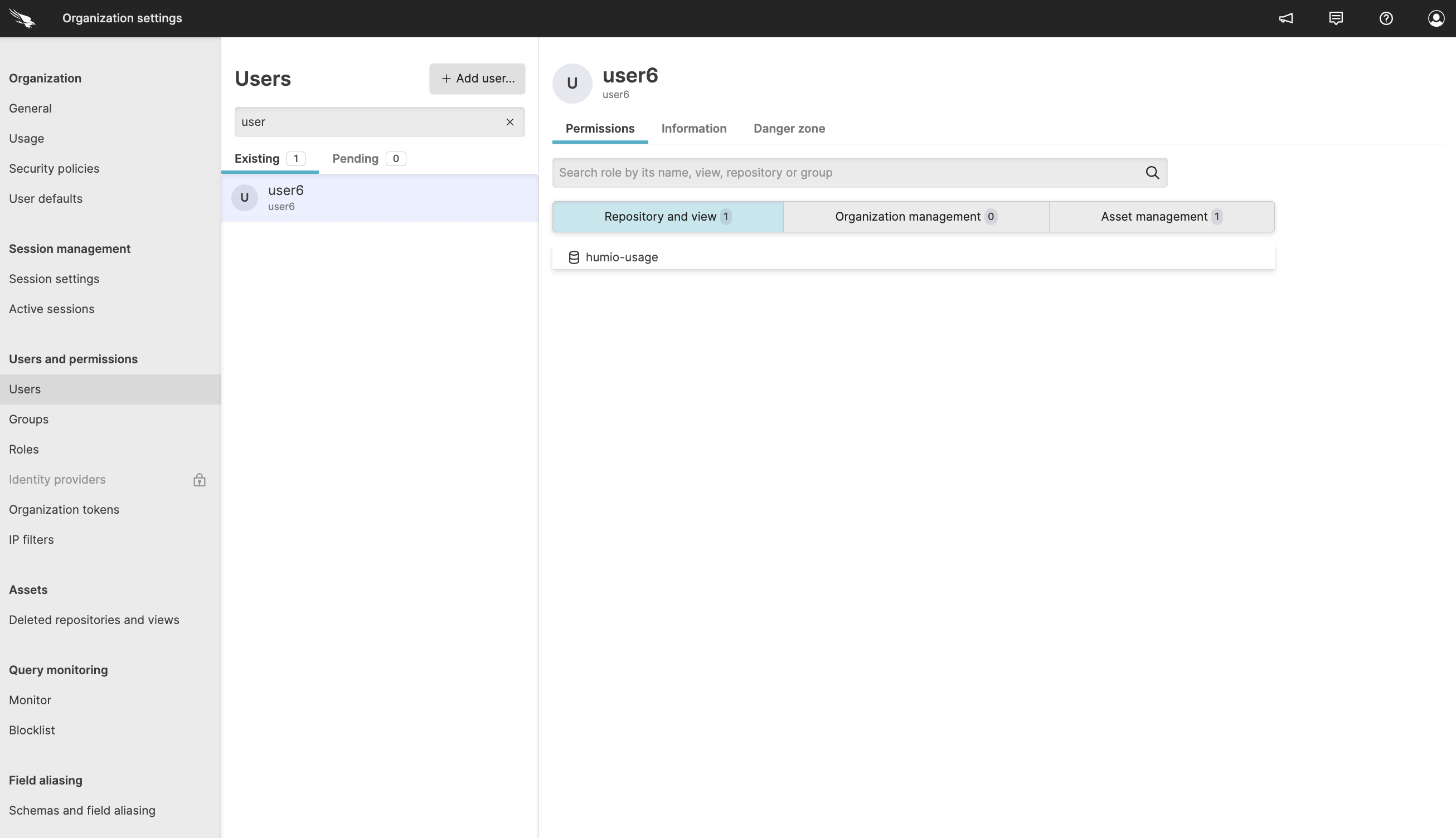 |
Figure 29. User Permissions
Select a repository from the Repositories and
Views page and click
on the menu.
To add a user to this repository, click under .
Click the button to add users and then you will be prompted to set their role.
For more information on user management, see Configure Security.
Connections
Select a repository from the Repositories and
Views page →
→ to
access the Connections
page.
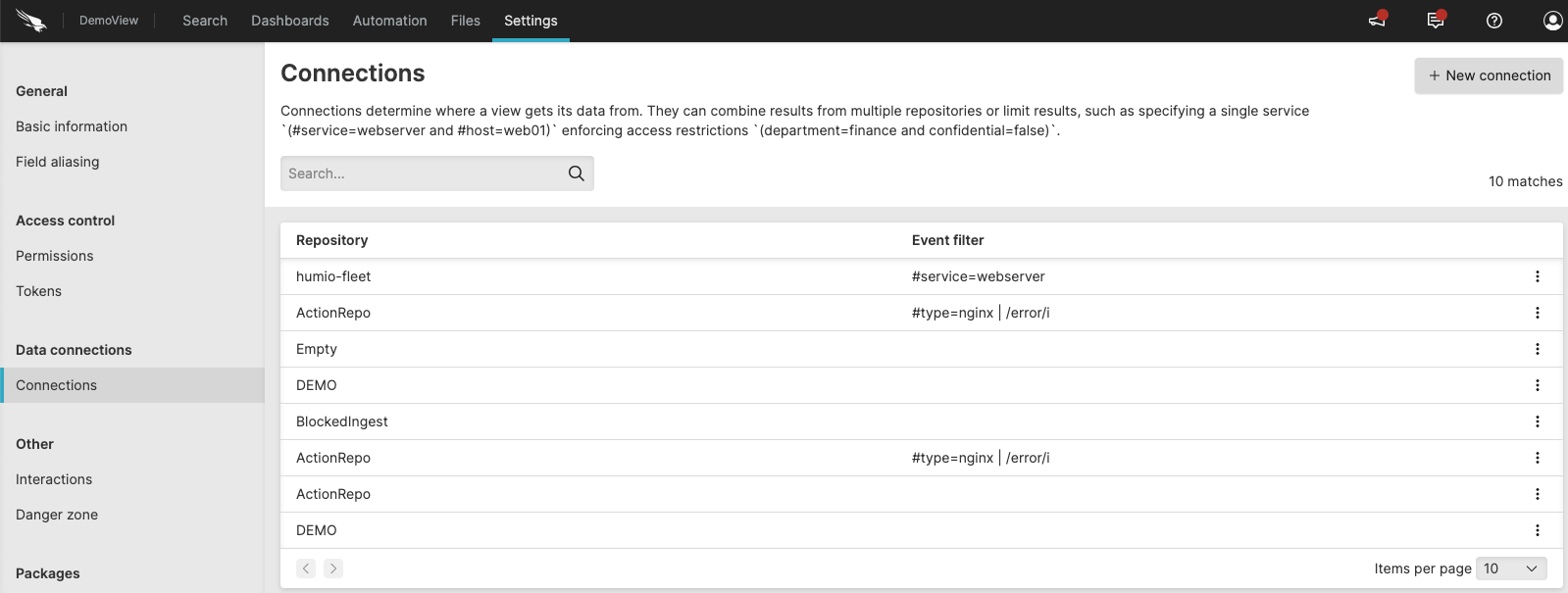 |
Figure 30. Connections
This setting is only visible when you create a view as it defines which repositories the view gets its data from.
You can use it to join results from multiple repositories or you can limit results to a single service, for instance:
#service=webserverand
#host=web01or implement access restrictions, for instance:
department=financeand
confidential=falseClick on the top-right to create a connection.
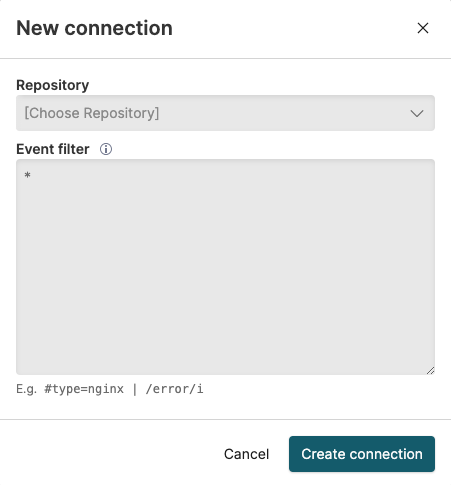 |
Figure 31. Create a New Connection
The filter query that you specify in the Event filter box is applied as a prefix to searches in the associated repository. This is what allows you to limit results to a subset of data or a particular service.
On LogScale Self-hosted, this setting is also used in Multi-Cluster Search, see Viewing an Existing Multi-Cluster View Settings for more information.
Repository Tokens
This page allows you to add new repository tokens, which are used for granting API access to all functions that relate to a specific repository. For more information, see Repository and View API Tokens.
Ingest Tokens
On this page you can manage the ingest tokens and assigned parsers, for more information on generating, editing and deleting tokens and assigning parsers to tokens see Ingest Tokens.
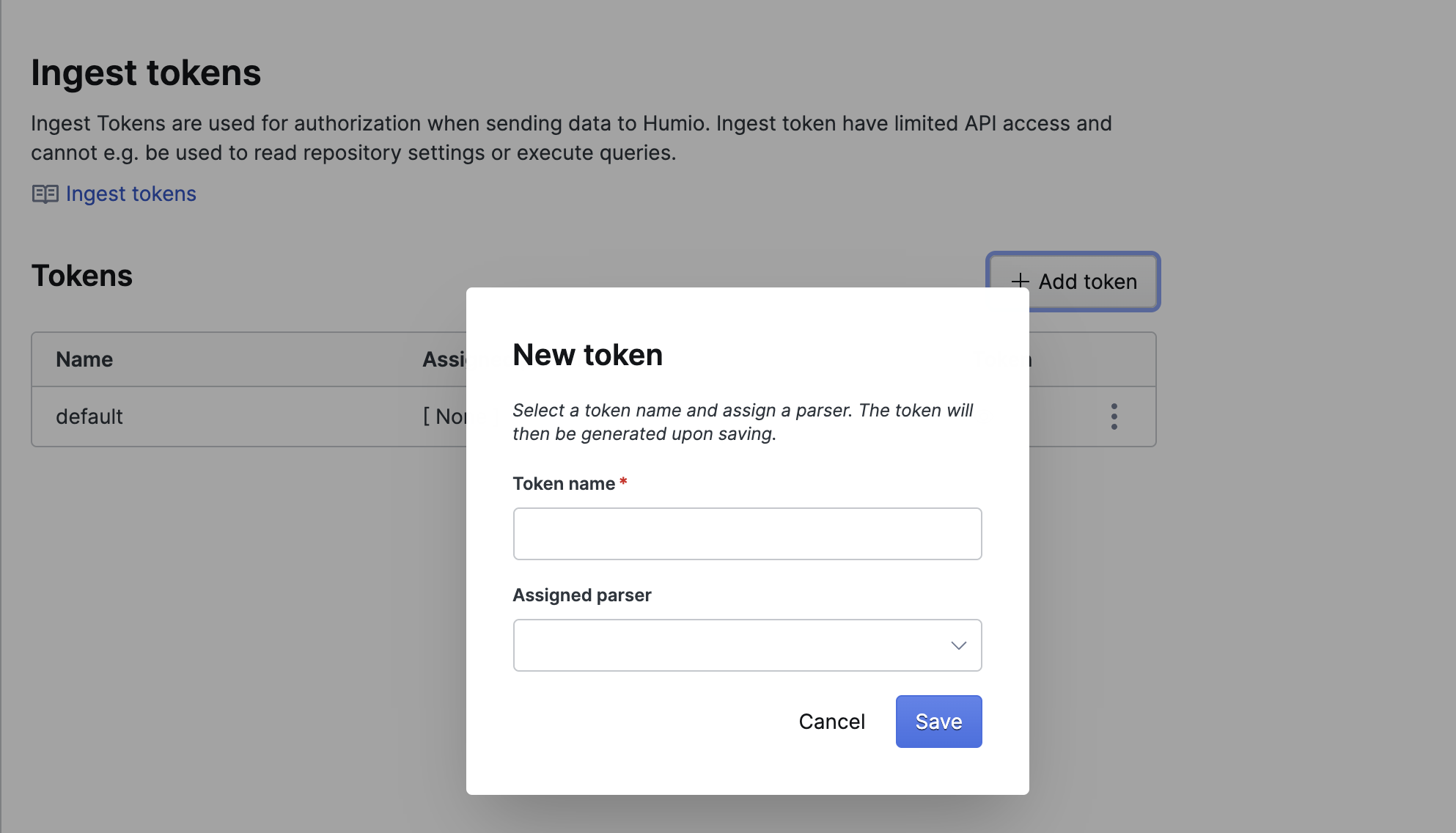 |
Figure 32. Ingest Tokens
Ingest Feeds
This page allows you to add and manage ingest feeds, which are used for ingesting data from AWS Cloud to LogScale. For more information, see Ingest Data from AWS S3.
CrowdStrike FDR
Use a Falcon Data Replicator (FDR) feed to ingest data from Falcon into your Falcon LogScale repository. You need to create an FDR feed in Falcon before doing anything on this page. For more information, see Ingesting FDR Data into a Repository.
Block Ingest
The Block Ingestion
page enables you to temporarily block ingestion for a short period of
time, after which it will be re-enabled. This can be useful in a variety
of situations where the level of ingestion and activity are causing
performance or reporting problems.
For more information, see Disabling Ingestion.
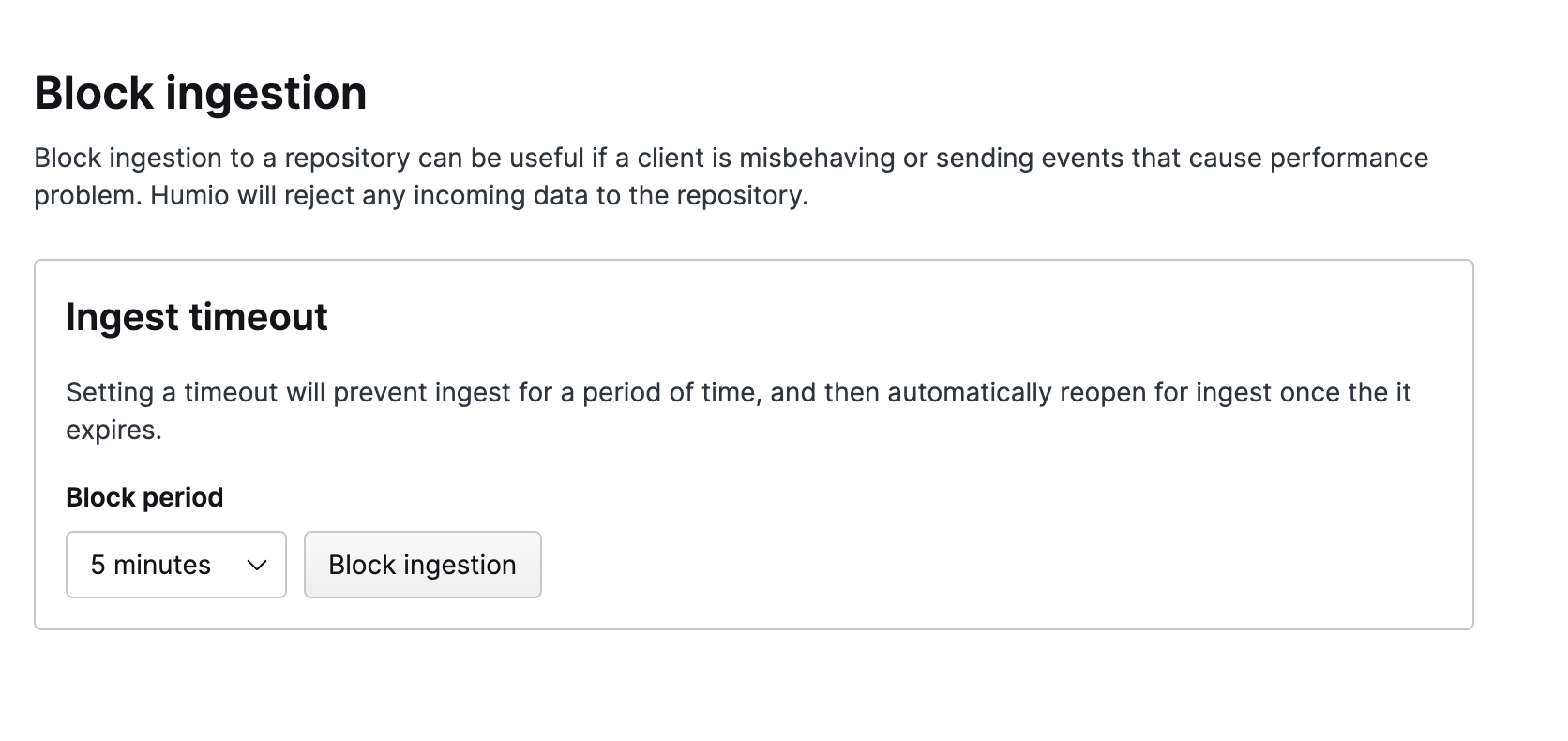 |
Figure 33. Block Ingest
Datasources
LogScale stores data in segments organized by the datasources and tags in the ingested data. These datasources are generated by a combination of the tags (#field fields) in the data. For more information on datasources and tags during ingest, see Tag Fields and Datasources. Datasources are created automatically, but can be deleted if a datasource is old and no longer needed and you want to save space.
Datasources can be tagged. You can create your own tags and assign them to events. See the Parsing Event Tags documentation page for more information on tags.
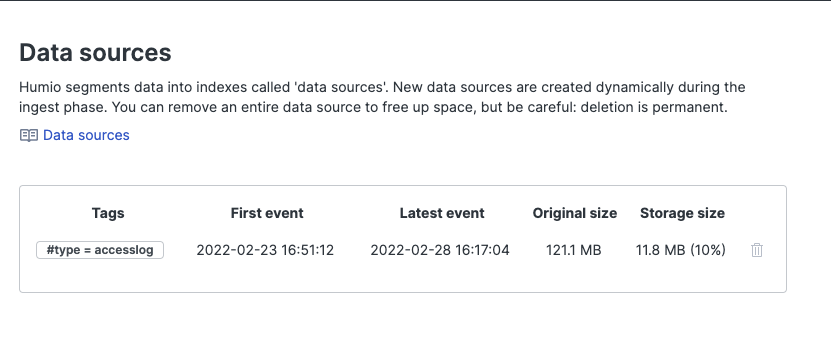 |
Figure 34. DataSources
Deleting a Datasource
Click the trash can icon next to the datasource to delete the datasource. This is a permanent deletion.
Tag Groupings
Tags in data (fields with the # are used
by LogScale to distribute data to allow for efficient ingestion
and querying perfomance. For each tag, a distinct datasource is created.
However, if the field has many distinct values (i.e. a high cardinality)
this can create a high number of distinct datasources which reduces the
performance. To alleviate this, the number of datasources can be limited
by setting a specific tag grouping, which limits the number of unique
tags to the defined setting.
The user interface for Tag groupings
allows you to view the current tag groupings that have been configured.
For example, two tag groups are defined in the screenshot below:
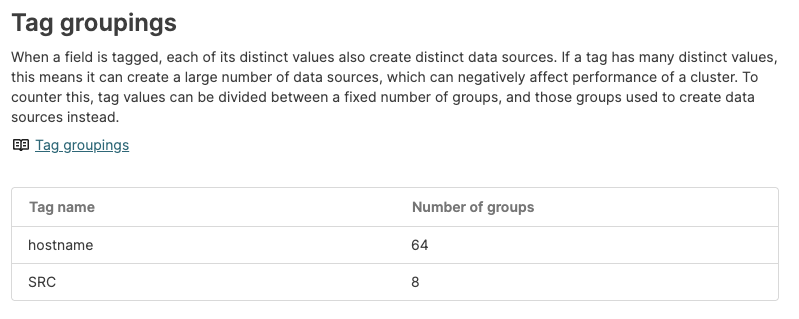 |
Figure 35. Tag Groupings
To manage and update tag groups, use the Update Tag Grouping API.
For more information on how tag grouping works, see How-To: Using Tag Grouping.
Listeners
This page is for managing ingest listeners. For more information, see Ingest Listeners.
Event forwarding
This page manages event forwarding settings. For more information, see Event Forwarding.
S3 archiving
This page manages S3 archiving settings. For more information, see S3 Archiving.
Danger Zone
The Danger Zone panel is so named because
the actions that can be taken here involve the deletion of data and
actions that cannot be reversed. Some actions don't include deleting
data, but can cause problems with the functioning of LogScale, leading
to major disruption of service — and can be difficult to resolve.
As a result, you should be very cautious when making changes here.
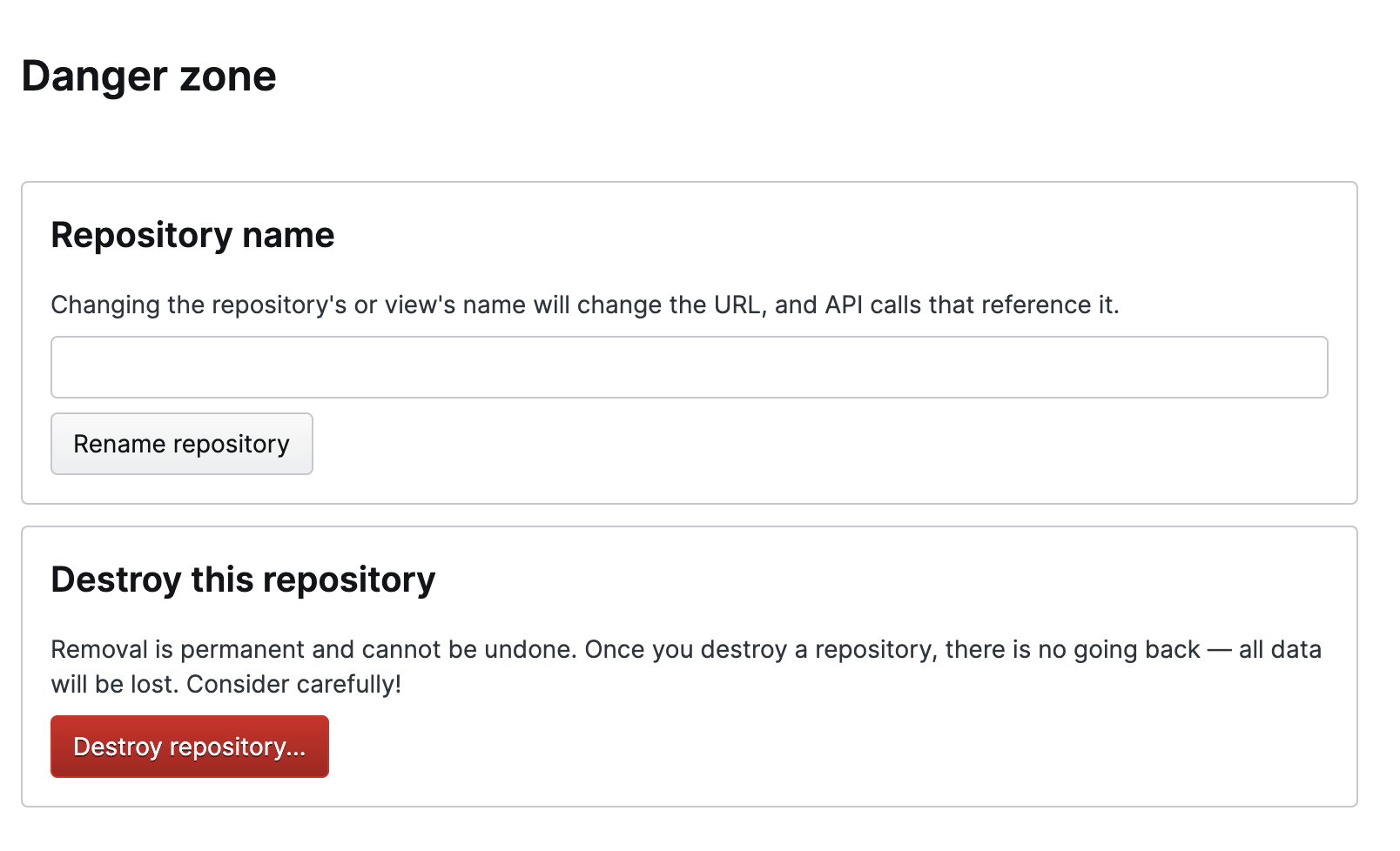 |
Figure 36. Danger Zone
The Danger Zone provides access to two
areas of the repository settings which have the potential to modify or
alter data:
Repository Name — enables you to change the name.
Important
This will change the URL and API calls associated with the repo, and may also affect the queries, automated actions, and RBAC associated with the repo.
Important
Destroy this repository — this option is not available to Cloud users. You must contact Support to delete a repository.
Packages
The Packages area allows you to install packages, verify the packages which are installed and create a custom package, see the dedicated Package Management documentation for more information.