Query Monitor
The Query Monitor enables live viewing of
queries being executed within LogScale, showing resource usage
and displaying detailed information about the process.
To access the Query Monitor page, select
from the menu. Then select
the under
in the left-hand panel.
The main page for the Query Monitor is
shown in Figure 4, “Query Monitor”.
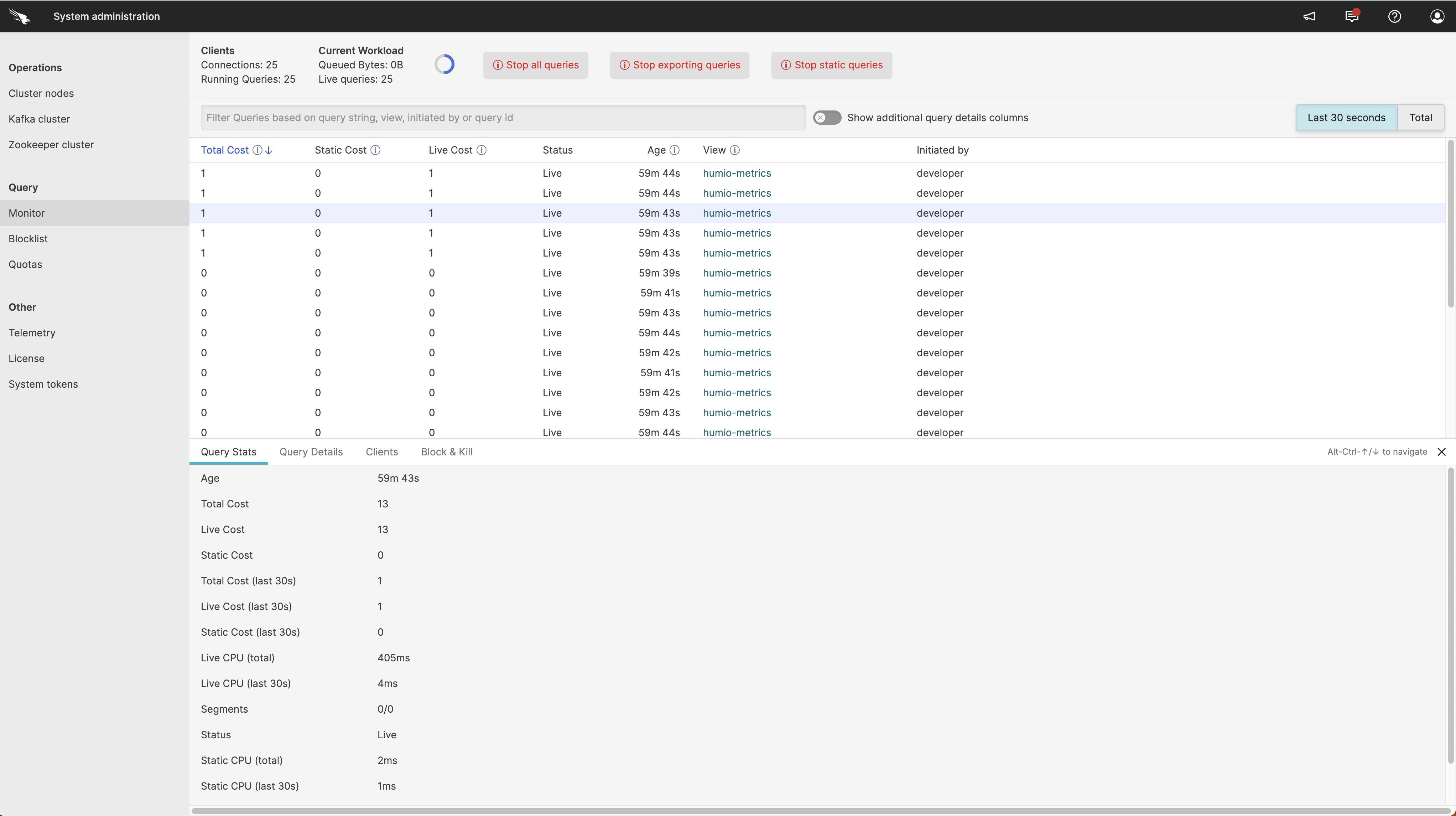 |
Figure 4. Query Monitor
Important
Streaming Aggregate Queries will not be shown in the list of running queries, and they are not canceled by the button. These queries can only be canceled by rebooting LogScale nodes.
Each query that runs in the LogScale cluster uses CPU and I/O
resources to varying levels. This is often referred to as the
Query work. The cost a query
can be used to compare two queries against each other, but not to rate
or identify the work for a single query. Using the Query
Monitor, administrators can determine which query has
the largest impact right now, or through the query's runtime. If a query
is using too many resources it can be temporarily killed or completely
blocked, prohibiting it from being run again.
The Query Monitor contains information
about the queries running in the cluster. The main part of the query
monitor is the tabular view that shows the top 1000 queries running.
The main display is divided into three sections, the summary data data at the top, the list of queries in the middle, and detailed panel of information for a selected running query.
The display of running queries is refreshed automatically every ten seconds; the redrawing blue circle at the top of the display shows the refresh information. The query data displayed can be controlled using the various Query Monitor Display Controls, including filtering the content and switching the showing recent (last 30 seconds) and all queries.
Query Monitor Display Controls
The information displayed in the main panel can be controlled using the buttons in the main display:
Last 30 Seconds/Total
These two buttons switch the display between showing only queries executed within the last 30 seconds, and the data for all queries executed.
This toggle enables three additional fields showing resource CPU and memory usage to be displayed for each of the shown queries.
Filter search
The filter search box allows you to filter the displayed queries by searching for specific information, including the query string, affected view, the user or the query ID. To filter the results, just start typing into the box.
Stops all running queries, immediately.
Stops queries that are exporting data or events.
Stops queries that are reading data from archived storage.
In addition to selecting the different queries directly, The Alt+↑ and Alt+↓ allow you to move up and down through individual displayed queries.
Query Monitor Summary Information
The top part of the Query Monitor shows
summary information for all the queries being monitored and displayed:
 |
Figure 5. Query Monitor Summary Panel
Clients
Connections
Shows the number of active query connections to the cluster.
Running Queries
Indicates the number of queries currently being executed. This includes all running queries, either through the search interface, dashboards or automations.
Current Workload
The workload shows the active workload on the cluster:
Queued Bytes
The estimated number of bytes what LogScale needs to load from disk in order for the currently executing queries to finish processing the history parts of the query.
Live Queries
Indicates the number of queries currently being executed that are waiting on data. This can be different to the number of running queries as differences in automated queries and dashboard refresh will not be included in this number.
Query Monitor Table List
The main table lists the currently running queries. The list of running queries can be sorted by selecting a specific column to change the displayed order. You can also filter and restrict the view using the filter box at the top of the list.
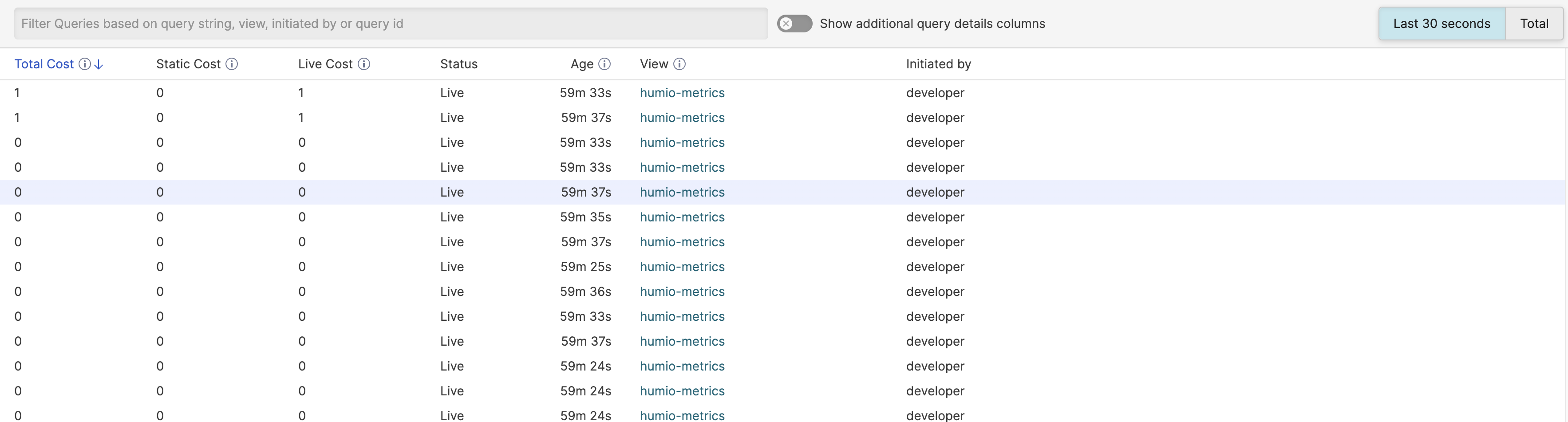 |
Figure 6. Query Monitor Table
The following columns are displayed:
Total Cost
Overall cost of executing the query in the last 30 seconds. The query cost is calculated as a combination of the CPU and memory requirements for a given query. The value can be used comparison cost value when comparing queries against each other. However, it is best to check the specific CPU and memory requirements to get an accurate idea of the resources being used.
Static Cost
The static cost of executing the query during the last 30 seconds. The static cost is a measure of the effort by the cluster to process historic (archived) data to perform the query.
Live Cost
The live cost of executing the query during the last 30 seconds. The live cost the time spent processing active (not yet archived) data.
Status
The current status of the query. A Live query is one actively being processed, for example as part of a dashboard or automation. Static queries are queries that have finished executing within a search.
Age
The time since the query was started. For a live query, this will show the time since the query was first executed.
View
Which dashboard, view or repository was used to execute the query.
Initiated by
The name of the user that initiated the query.
If the Show additional query details columns toggle has been enabled, the following additional columns are shown:
Static CPU
CPU time spent fetching archived data to execute the query.
Live CPU
CPU time spent processing active data for the query.
Total MA
Total Memory allocated in order to complete the query.
Selecting a given process from the list allows you to display more detailed information. This information is shown in the bottom panel: