Manage Roles
Security Requirements and Controls
Manage userspermission
Manage and customize user roles in LogScale, including creating new roles, setting permission levels, and modifying existing predefined roles like Reader, Admin, Member and Deleter. Users with Organization Owner status or appropriate permissions can access the Roles page to configure role-based access controls, assign granular permissions, and view aggregate permissions across multiple roles to maintain security best practices.
All roles available and the permissions granted via the roles are displayed
in the User Interface in the
Roles page.
Depending on the permission level chosen, you can assign different permissions for any new role you create. For example, you can create an Organization management role type and name it, say, "Operations", which grants permissions such as the capability to view all internal notifications, or to manage other users.
LogScale comes with a predefined set of roles — Reader, Admin, Member and Deleter. All of these roles (except Reader) may be customized to your specific needs. Keep in mind that it is generally a good idea to grant as few permissions as possible and to add more as needed.
See the full list of available permissions along with descriptions of their usage at Repository and View permissions.
To get a list of roles with your own application, use the GraphQL API, in particular the roles() query. For information on a specific role, use the role() query. It will give you a list of roles, which permissions granted with the role and which users have been assigned the role.
Note
You need to be an Organization Owner on Cloud or a root user on
self-hosted installations to have access to the
Roles page and assign
roles to users. Or you need to have the
Change user access
permission:
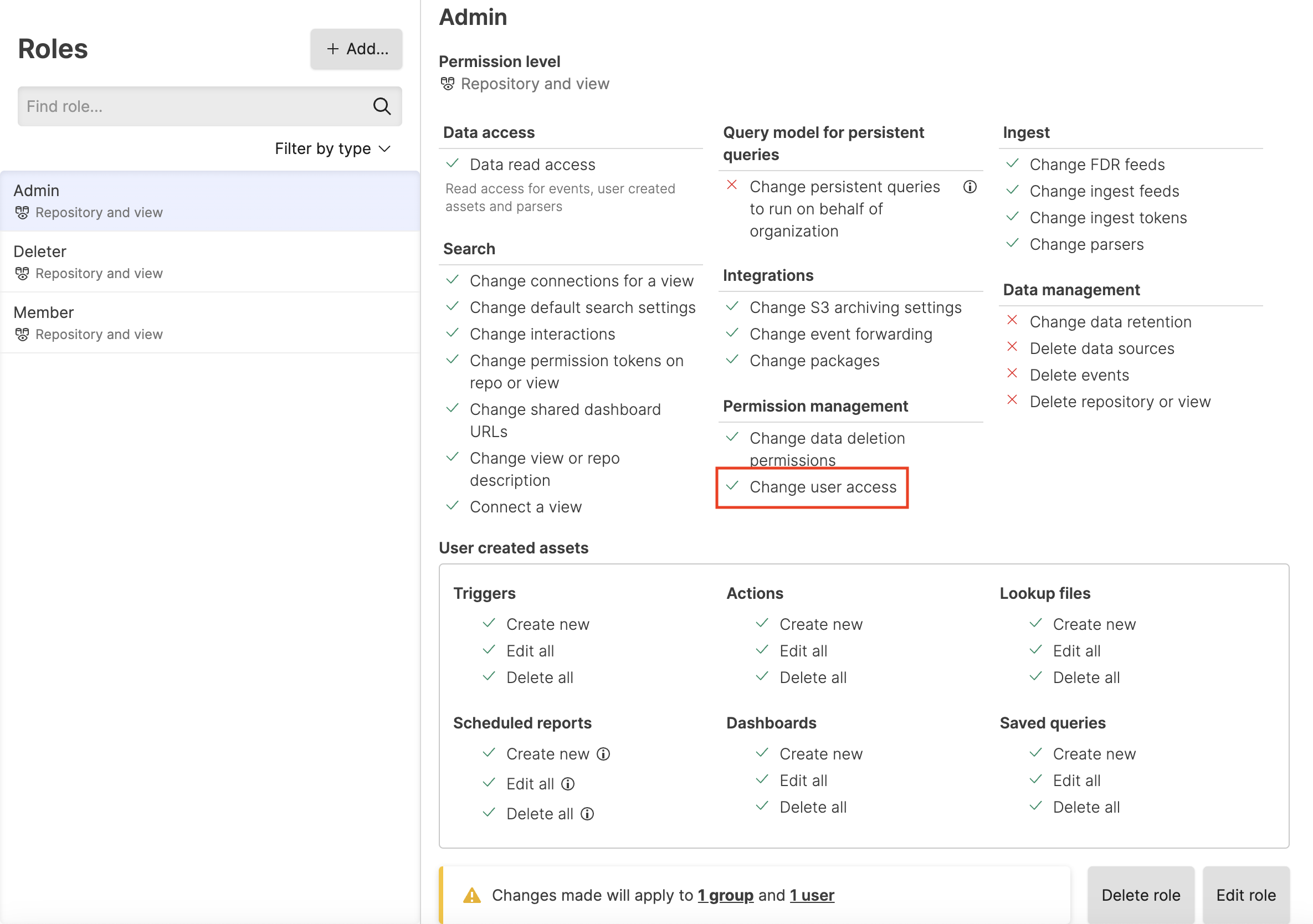 |
Figure 126. Change User Access
Add a role
To add new roles or customize existing roles, do the following steps:
Click on the user menu icon and select Organization Settings → Roles.
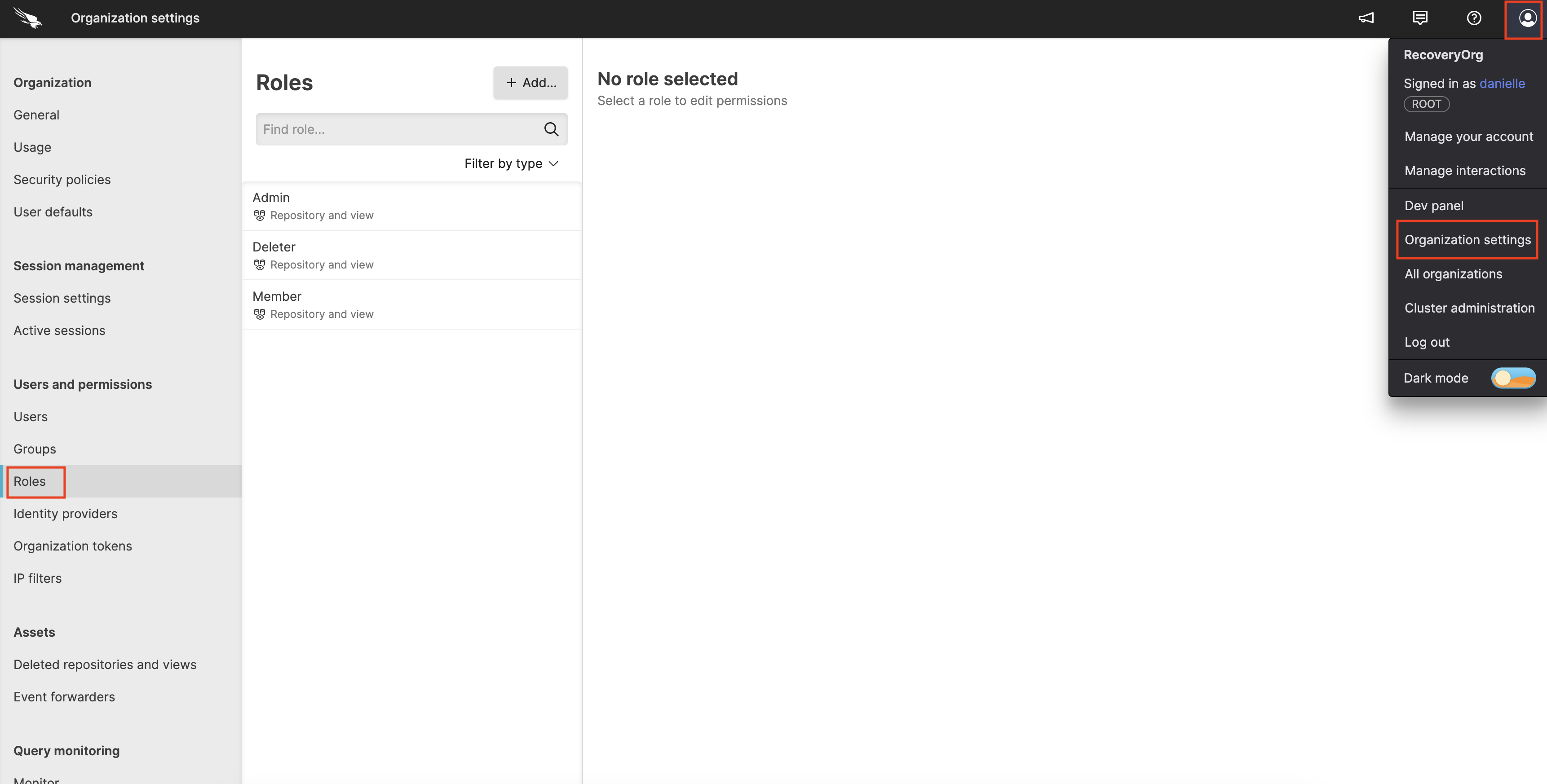
Figure 127. Roles
Click + Add to create a new role; enter a name for the new role such as "Operations", and select a Permission level for the role, for example, Organization management.
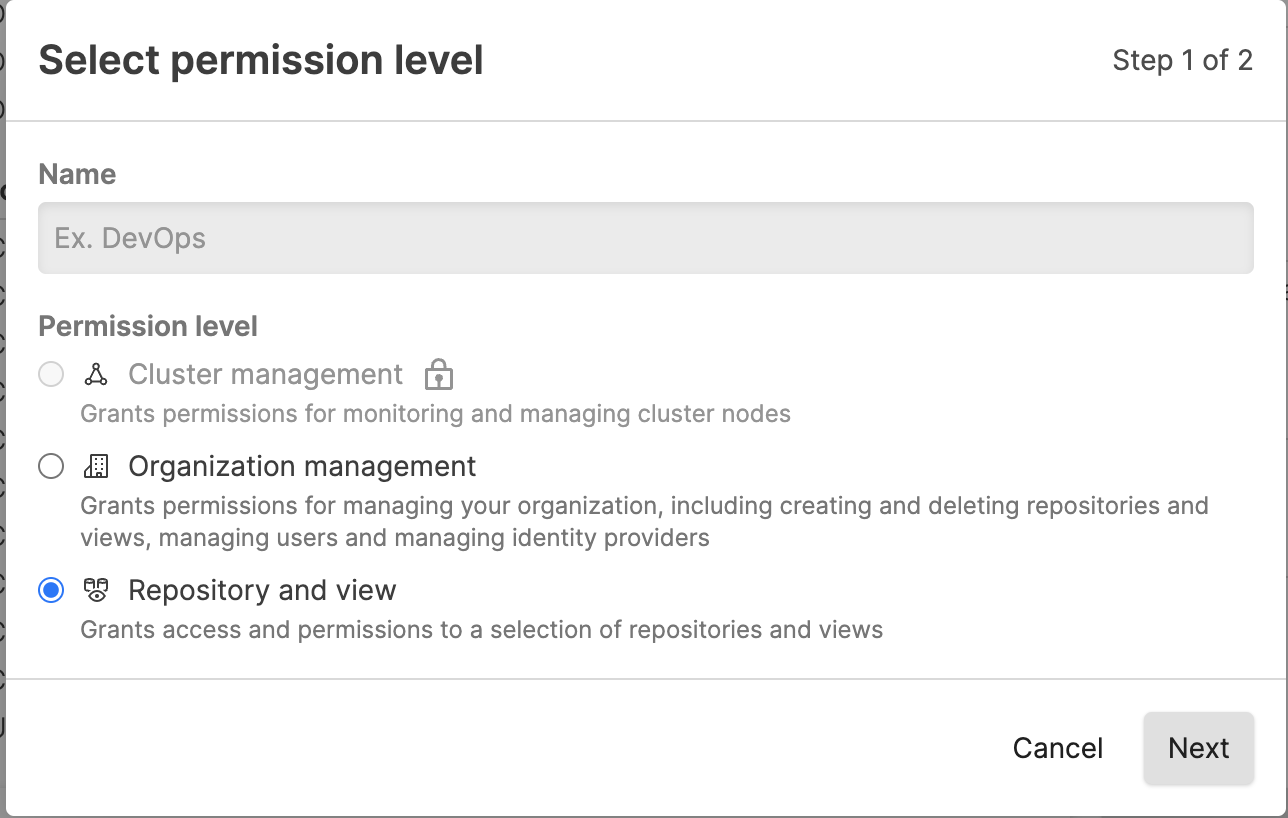
Figure 128. Add Roles
Set the permissions for the role. For example, if you wish to create a strictly read-only role, select the Data read access checkbox and nothing else, then click Create role:

Figure 129. Assign Permissions to Roles
User asset permissions allow users with this role to create, edit, and delete the asset types selected. Asset permissions can only be added to a role if the role has
Data Read Access; otherwise they are not available.The new role can now be assigned to groups via the
Groupspage of the User Interface, where you are prompted to configure the permission levels for a group — see Figure 116, “New Group Created”.
Change role permissions
You may change an existing role and its permissions, as well as delete the role. To make these changes, do the following:
Starting from the beginning, click on the user menu icon and select Organization Settings → Roles.
Select the role you want to change and click Edit role as shown in this screenshot.
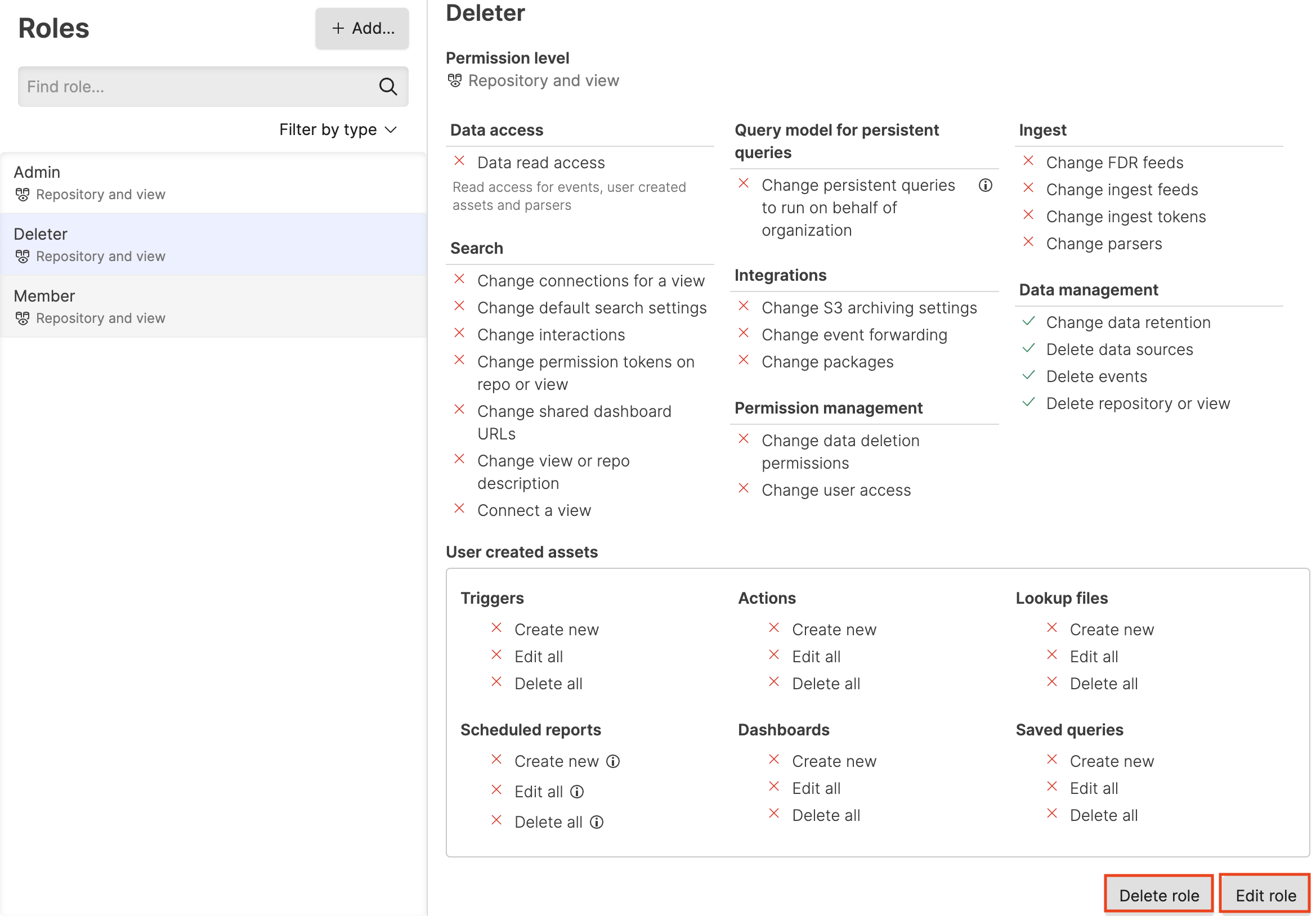
Figure 130. Customize or Remove Roles
Next, a dialog box will appear showing all of the permissions available for the role — with a check mark next to the ones given. Check the permissions you want to add; uncheck the ones you want to revoke for the role. When finished, click Save changes.
To delete a role, instead of clicking the Edit role button, click Delete role, as circled in red in the screenshot above.
To edit a role using the GraphQL API, use the updateRole() mutation. To delete a role, use removeRole(). You'll need the unique identifier for the role, though for both mutations. To get that before make changes or deleting a role, use the roles() query.
Aggregate permissions
Security Requirements and Controls
Manage userspermission
When you have defined more than one role under a Repository and View, Organization, or Cluster, you can get a combined view of the available permissions for all roles — all permissions in a specific repository, for example. This gives you an overview if you want to know exactly which permissions you have.
Click on the user menu icon and select Organization Settings → Users.
Select one of the users that have multiple roles assigned and click on a repository.
Click Show aggregate permissions in the Permissions panel.
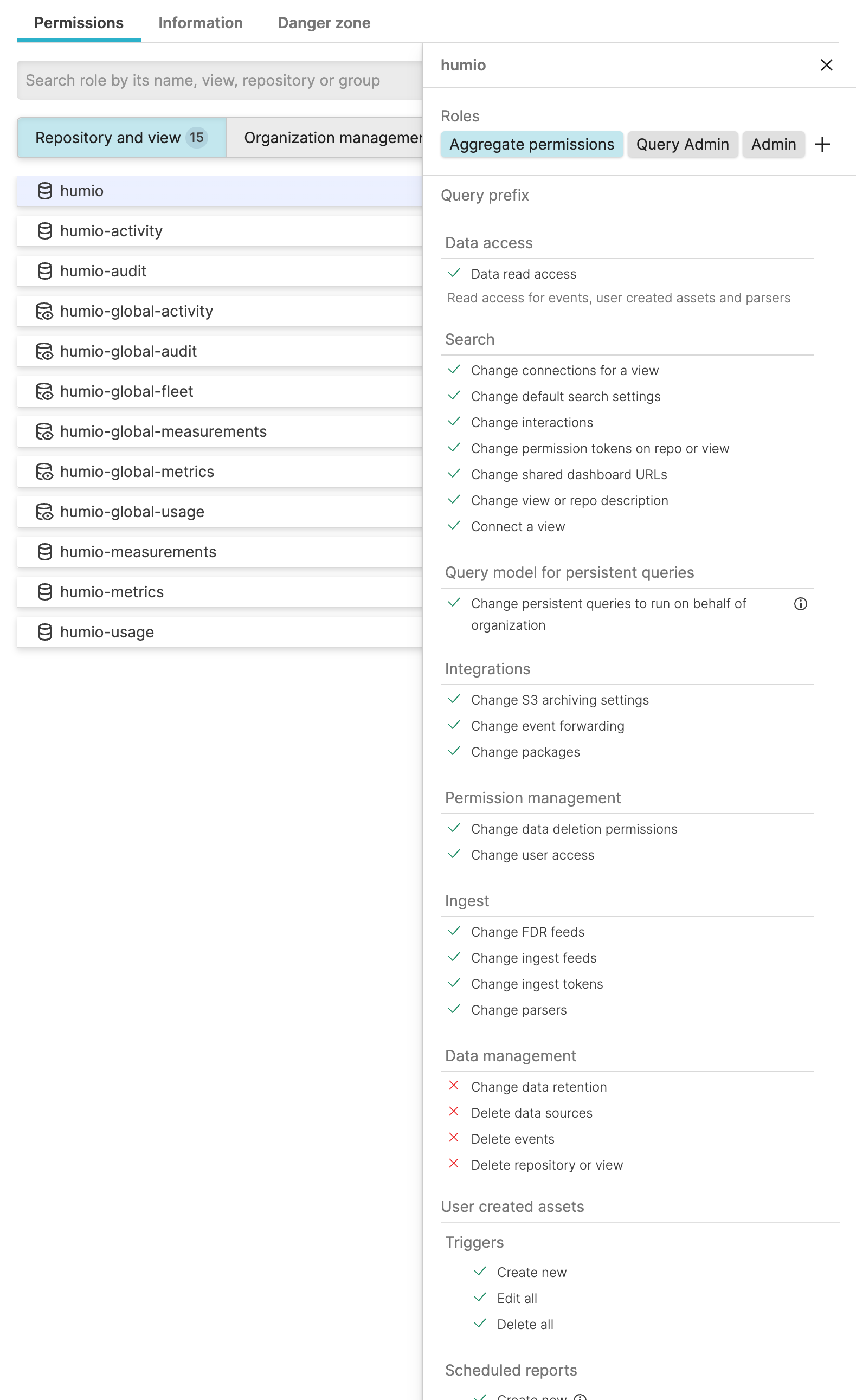
Figure 131. Aggregate permissions
You can always select a single role instead to see only the permissions for that role.
Note
When evaluating aggregate permissions and the query prefix set for roles, all assignments are evaluated, and their prefixes are put together in an OR statement, for example, prefix_A OR prefix_B OR prefix_C. The roles with an empty prefix are considered as having the prefix * (wildcard).
If a role assignment does not grant read access to the view, then the query prefix is ignored when computing the combined prefix because this means that role assignment doesn't grant access to query in the view at all.