Manage Dashboard Parameters
Security Requirements and Controls
Change default search settingspermission
Dashboard parameters allow you to interact with dashboards for performing filtering and assisting with drill-down dashboards.
By providing parameters within your queries, you allow your users to configure values in the dashboard for the fields you have defined as being the parameters for that dashboard.
Here is an example of query with parameters on the Search page:
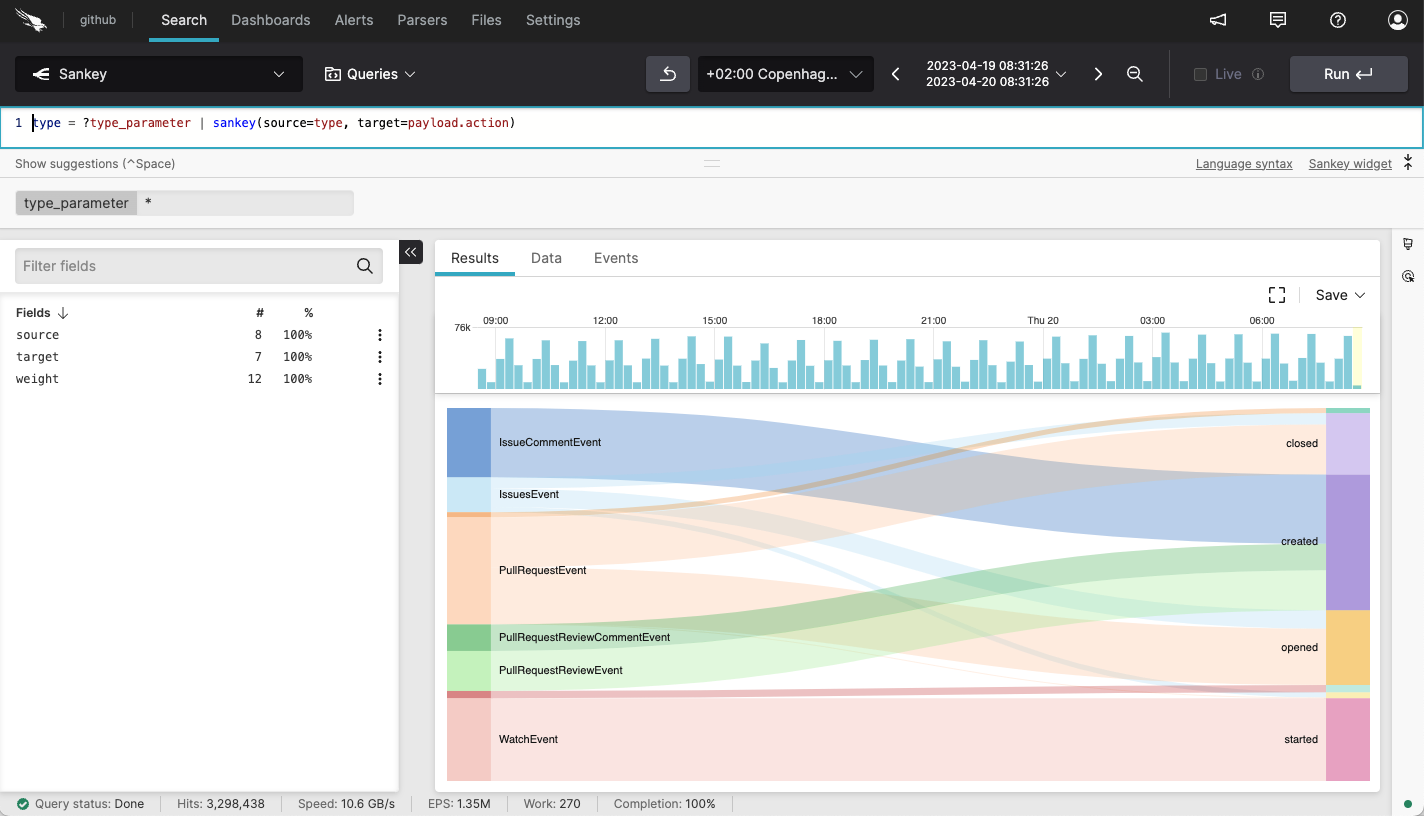 |
Figure 175. Query Parameter in Search
All parameters are added to the query using the
?parameterName syntax, like
?type_parameter in the example above. For
more details on the syntax used for query parameters, see
User Parameters/Variables.
When you specify some parameters in your query, they automatically appear as options during searches, and the query is used as part of a widget within a dashboard. This allows for users to submit values for a query without the need to edit the query directly.
Here is an example of parameter on the
Dashboards page, where the
?loglevels parameter is autodetected and
used by a widget within the dashboard:
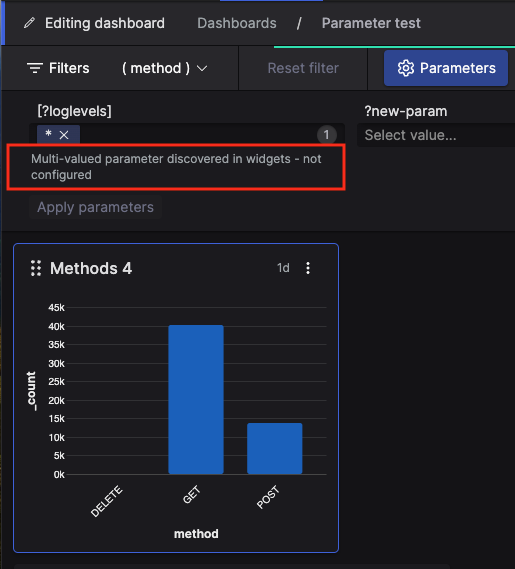 |
Figure 176. Autodetected Parameter
Parameters with the same name used in different widgets use the same input field. This allows you to impact multiple widgets with a single parameter input field.
Therefore, dashboards show a list of unique parameter names across all widgets, meaning that, if multiple widgets use the same parameter — like in the example figure above — the parameter name will only appear once on top of the dashboard. This also means that, whenever you need to delete a parameter that multiple widgets have in common, you will have to remove it in each single widget.
If a new widget uses a different parameter name instead, then this new parameter name will be added on top of the dashboard, and will of course use a different input field.
See Adding Parameters and Configuring Dashboard Parameters for how to set parameters in the UI and the syntax usage.
There are different kinds of parameters you can set, find them all described at Parameter Types.
For examples of parameters used in dashboards, see Examples of Parameterized Dashboards.
Adding Parameters
Security Requirements and Controls
Change default search settingspermission
You can add dashboard parameters in two ways.
Specify parameters in the search query:
Insert one or more parameters in the query using the syntax
?parametername, for example:logscaleComputerName = ?ComputerName AND AgentIdString = ?aid AND CustomerIdString = ?cidIn this query, the
?ComputerNameparameter works as a single-value parameter, meaning that it allows to submit a single string as its value.To support specifying one or more values, you can make it a multi-value parameter by using an array syntax instead:
logscalein(ComputerName, values=[?ComputerName])For more explanations on how multi-value parameters are used, see Multi-value Parameters.
Run the query, select the desired widget type and add the widget to the dashboard: parameters set in the query are automatically discovered on the dashboard and will appear at the top of it.
Add parameters directly from the dashboard interface:
Click the pencil icon on the top right to take the dashboard in Editing dashboard mode.
On top of the dashboard, click and add a new parameter.
Parameters are displayed in the top panel: for better organize the information in dashboards, you can use a Parameter Panel Widget and move parameters out of the top panel and onto the dashboard area.
For the added parameters to take an effect on the widgets, edit your widget queries to include the parameter syntax, as described in Specify parameters in the search query. Similarly, to remove parameters select from the ⋮ icon of each single widget and delete all
?parameternamesyntax references from the widget's query.
By default the input fields are plain text fields that default to * — as on the Search page. But you can customize parameters to make them easier to use, and to select values in a dropdown instead of manually typing. See Configuring Dashboard Parameters for information on how to configure and customize your parameters.
Configuring Dashboard Parameters
Security Requirements and Controls
Change default search settingspermission
To configure your parameters in a dashboard:
Click the button with the pencil icon on the top right to take the dashboard in Editing dashboard mode
Click the button, this will show all available parameters.
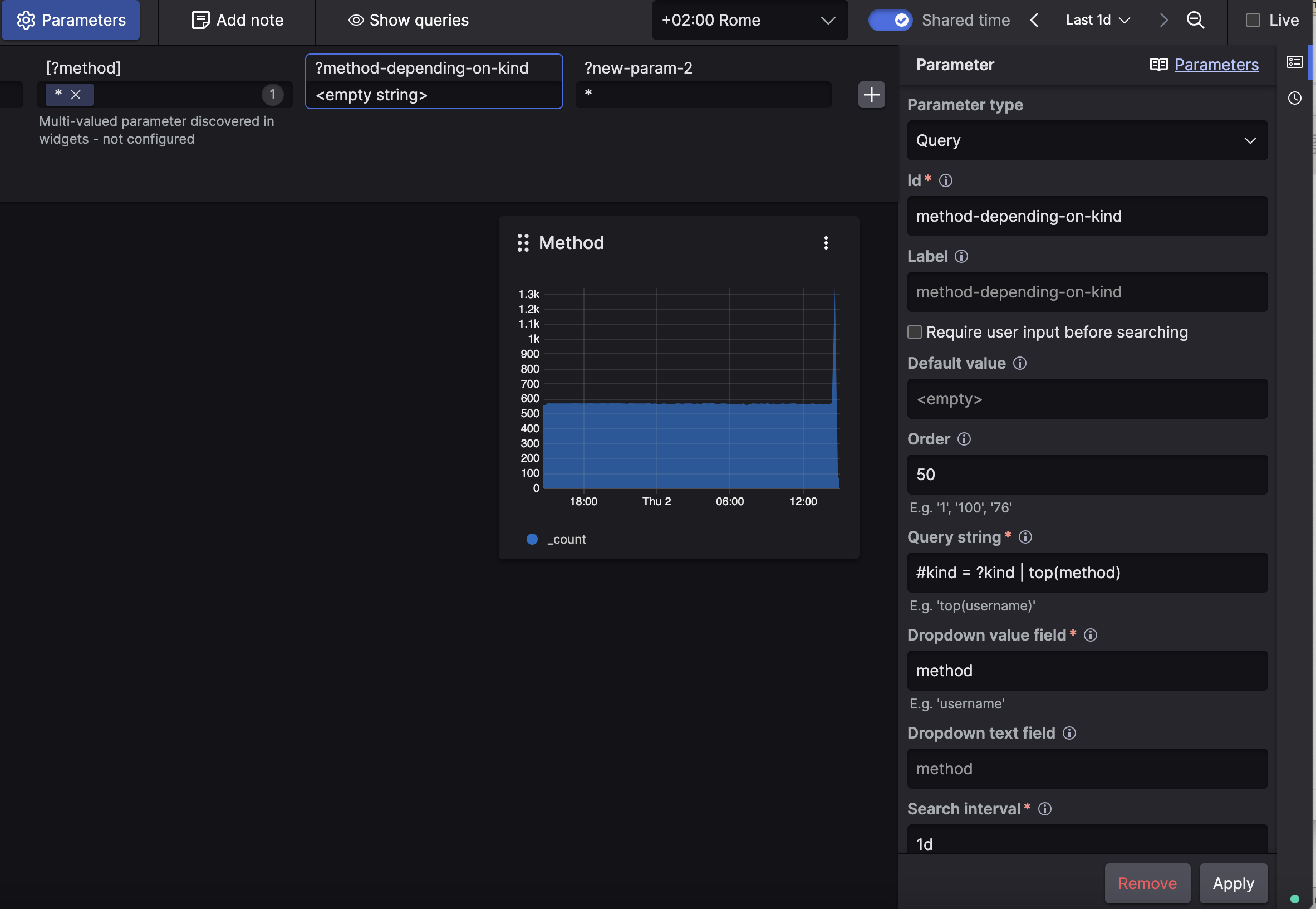
Figure 177. Configuring Parameters
Click on a parameter and fill in the Parameter side panel to configure its settings:
Parameter type choose the type from a list of available Parameter Types.
Id — is the ID of the parameter. For example,
userwill mean you use?userto reference it in a query. When changing the ID of a parameter you will have to manually update any queries using it to reflect the name ID.Label — is the name displayed in the list of parameters. For example,
Usernamein place of?userwould best suit to appear on the dashboard.Require user input before searching — allows preventing the dashboard from executing any queries on page load until the user provides a value to the parameter.
For example, in the query:
logscalein(method, values=?method)widgets that use the
?methodparameter will defer their execution until their user has entered a value, likeGETorPOSTin the parameter's input field: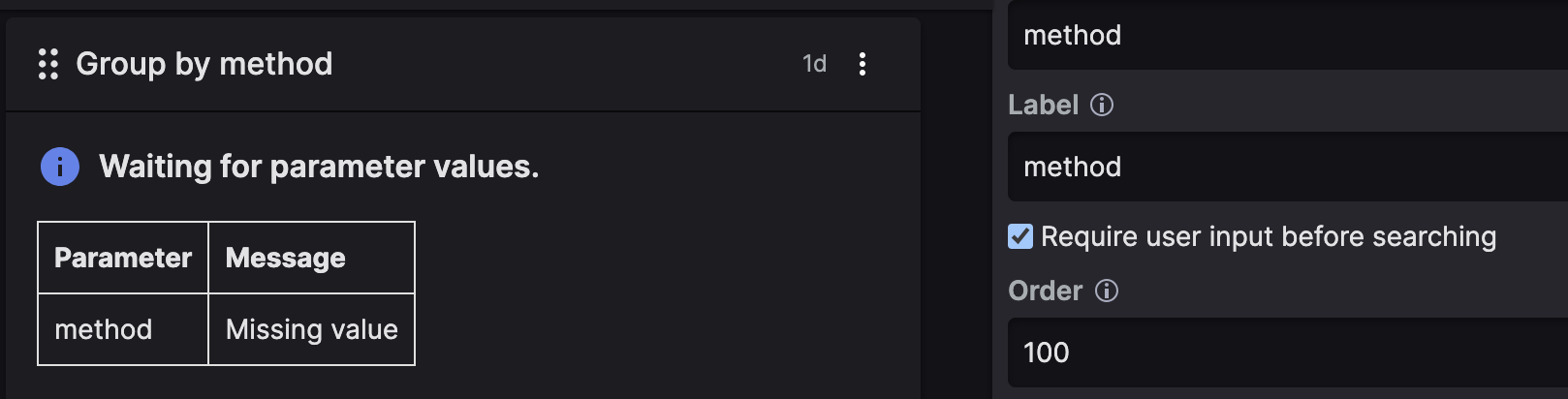
Figure 178. Required User Input
This setting can be useful in cases of long and complex queries — too expensive to run and returning a huge amount of data not meaningful for the purpose of the search.
For example, you may want to run a query limited to a certain group of emails from your data: you can do this by setting an
?emailparameter and then run the search only when certain email domains are entered as input for that parameter.If this setting is unchecked, you need to specify the default value used in the queries on the page load. You can use wildcards like
*to use all values.Default value — allows you to set the default value the parameter should have. You might want to set, for example,
productionfor an?environmentparameter. Use the wildcard*as the default to match everything, which means no filtering.Order — controls the order of parameters on the dashboard page. Lower values will bring the parameter to the first positions on the list. For example,
1or100.Width — expands the parameter's name panel.
Invalid input patterns — enables to provide one or more regex patterns that define invalid inputs to the parameter. For example:
[^\d]match anything but digits (numbers)^bad$match the specific stringbad\*match any string containing*— disallows all glob pattern matching, like inbad*.^\*$match the specific string*— disallows wildcard parameters.
Invalid input message controls the message shown to users of the dashboard when they input something invalid to the parameter.
Other settings specific to different parameter types. For details on these settings, see Parameter Types.
Warning icons next to a parameter's name inform about the parameter's state:
Figure 179. Parameter State Icons
A red state icon will inform of any wrong configuration in the parameter's settings, whereas a yellow icon might indicate that the parameter is inactive and needs to be added to queries for it to have an effect on the dashboard.
Parameter Types
While you are Configuring Dashboard Parameters, you can choose one of the following parameter types from the Parameter Type dropdown menu:
— allows you to just type a free text input as the value you want to filter or aggregate.
— creates a dropdown list of values based on the results of the query. The dropdown list is created as single or multiple choice, depending on the parameter being single or multi-valued (see examples at Examples of Parameterized Dashboards).
parameters have unique settings in addition to the common settings for all parameter types:
Query string — mandatory setting that must contain a LogScale query. For example, you may want to fill in this field in conjunction with an aggregate function. Like in the Query Editor, this field highlights syntax and suggests completions to help you write queries. See some examples of parameters used in queries at Examples of Parameterized Dashboards.
Dropdown value field — is the field in the results that should be used as the value for items. For example,
userId. This is a mandatory field.Dropdown text field — is the field in the results that should be used as the display text of items. For example,
email.Search interval — sets how far back in time to search for values. This is always relative to the current time. For example,
5m,2h. This is a mandatory field.Use dashboard search interval checkbox — makes the query for this parameter use the same time interval selected for the dashboard.
Query-based parameters can contain references to other parameters, see Parameters Referenced in Other Parameters for more information.
— provides a fixed set of options, it is good when you have a small set of fixed values that will fit into a dropdown menu. If there are too many values to use this parameter type, however, the parameter may be a better fit.
parameters have unique settings in addition to the common settings for all parameter types:
Values and labels — List of comma-separated values. For example,
server1,server2,server3, with optional labels such asProd,Test,Staging.
— LogScale supports uploading of CSV and JSON files for use with the
match()function in queries, but those same files can also be used for populating parameters. File-based parameters can contain references to other parameters, see Parameters Referenced in Other Parameters for more information. File validation displays a warning if the lookup file used as a source of suggestions was deleted.parameters have unique settings in addition to the common settings for all parameter types:
File — Insert the name of a file. This is a mandatory field.
Value field — The field in the file that should be used as the value. For example,
userId. This is a mandatory field.Label field — The field in the file that should be used as the display text of items. For example,
email. Allows you to configure the values that will appear in the UI when you select the value for the parameter, but it is still the value field that determines what data goes in the query. If no labeling field is configured, the UI will display the actual values.Value filters — Limit entries coming from the file by configuring some fields; for example, country, with a certain value, like
Germany. You can use parameters as values and specify multiple values by separating them with commas.
Take this configuration as an example:
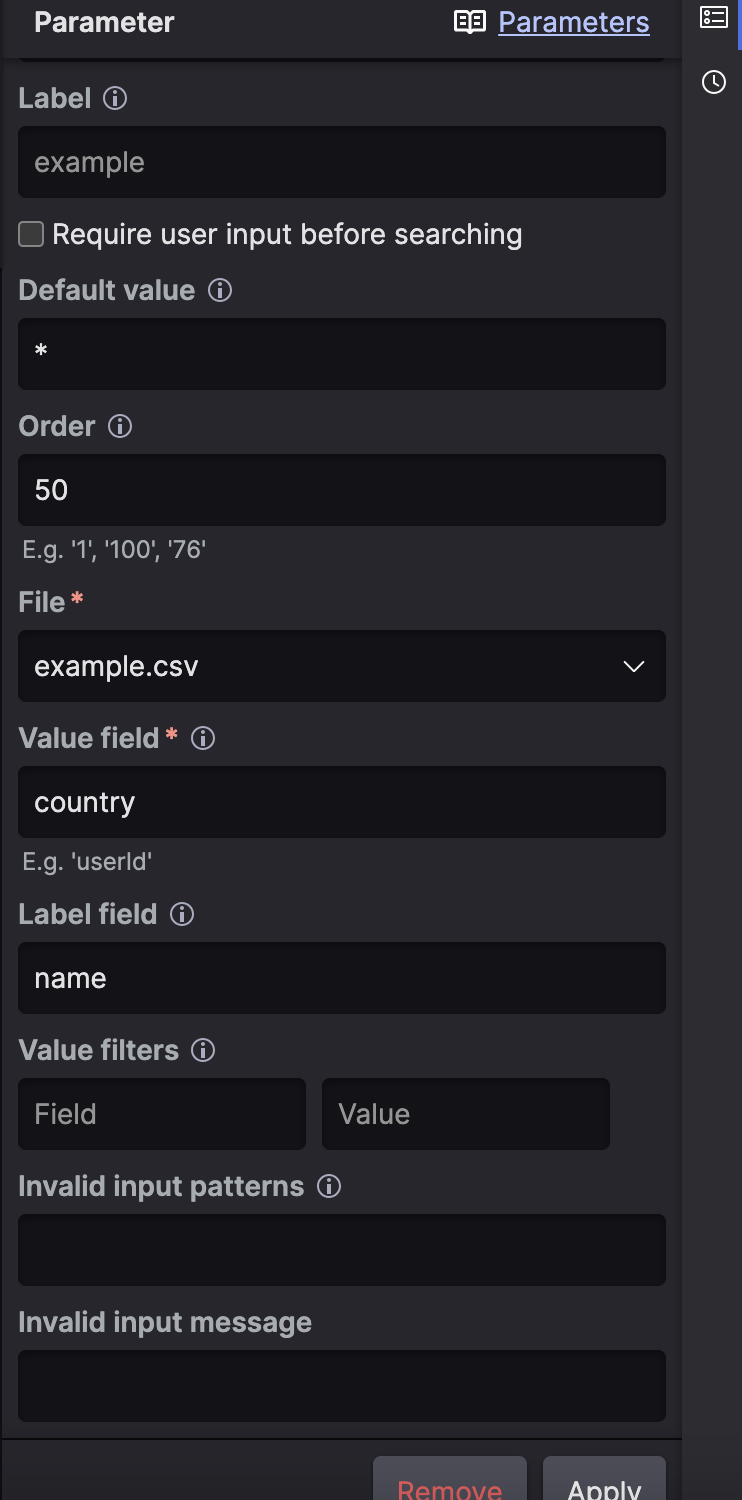
Figure 180. File Based Parameter Configuration
If
example.csvhas these contents:csvuserid,name,country 1,alice,us 2,bob,ukThen using the parameter in the dashboard looks like this:
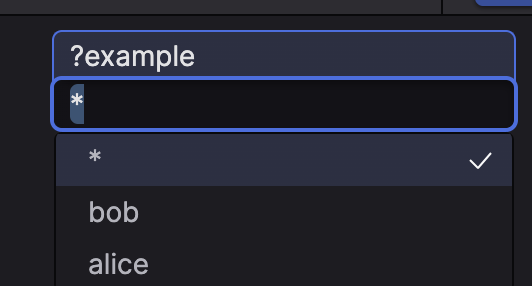
Figure 181. File Based Parameter Output
Selecting the
aliceoption will insert the value1into the parameter, and the same forboband2.We can also use the Value filters configuration to hide entries from the output. Since
example.csvalso contains acountrycolumn, we can specify that we only want users from, for example, the USA: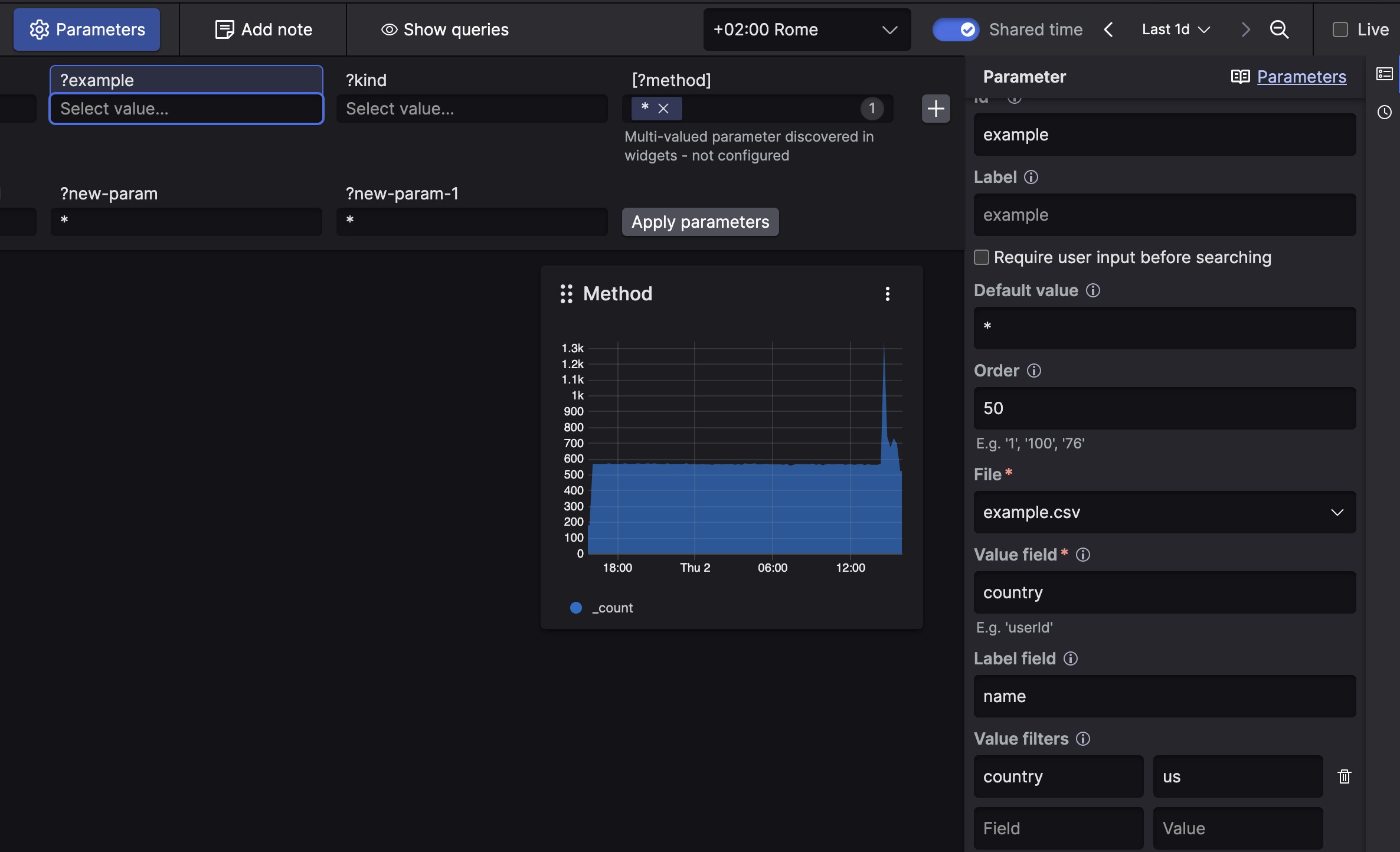
Figure 182. File Based Parameter with Static Filter
This would remove
bobfrom the output, but we can also specify multiple values, separated by comma, or use a parameter as input. Using a parameter is the same as writing out the options yourself, but you type, for example,?countryinstead ofus, and you will get the appropriate options.
URL
When parameters are assigned, they will be added to the URL and you can share a link to a dashboard configuration simply by sharing the URL of what you are looking at.
This can also be used to integrate with other systems, where you can construct dashboard URLs that contain parameters. This could for instance be an IP found in an external system that you want to look at logs for on a dashboard.
Notice that URLs use the syntax
dashboards/<dashboard-id>?$param1=value1&$param2=value2
where parameters are denoted with the $
sign instead of the ? (like you use in
queries). This is because ? is a
reserved character in URLs.
Tip
Use Dashboard Link to bind values from the data to parameters for a dynamic integration with related LogScale dashboards.
Examples of Parameterized Dashboards
Single-value Parameters
Let's take an example where you want to create a dashboard that monitors status codes for the different hosts available in the data, and you want to match these codes within a certain range — subnet — of these hosts. Let's assume that events are attributed with the following fields:
host — the hostname of the server.
status_code — the status code of the entry, such as
200.
Go to the Search tab from the top menu bar and enter a query like the one below:
logscalecidr(host,subnet=?Subnet) | status_code > ?StatusCode | groupBy(host)The query contains two parameters:
?Subnet, and?StatusCode.Run the query to produce a
Bar Chartwidget with one series per subnet host, counting how many errors occur.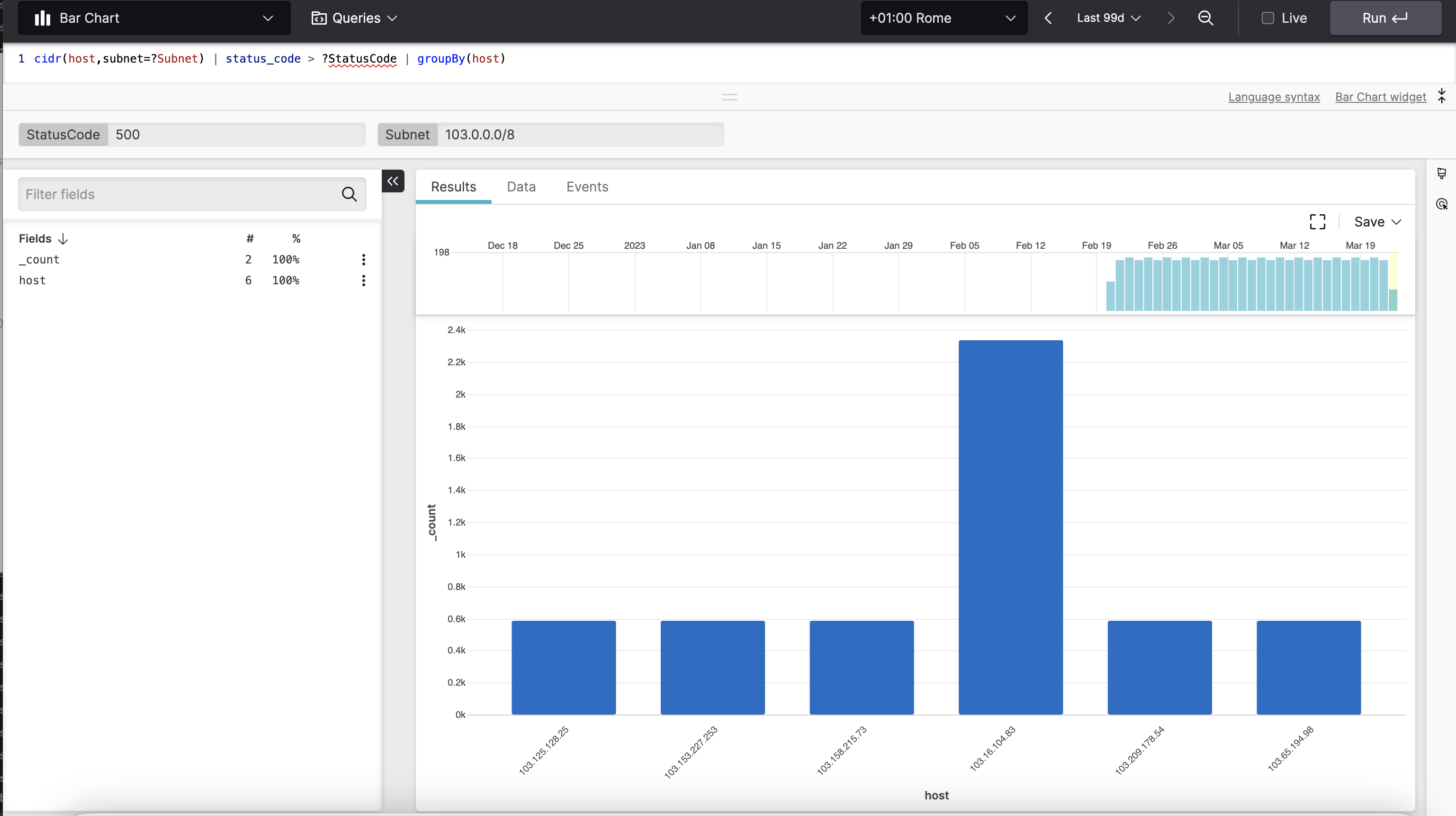
Figure 183. Parameters in a Query
Set the
?StatusCodeparameter to500, and the?Subnetparameter to103.0.0.0/8for example, and run the query again to show results for only those hosts having registered a500status code in that specified subnet.
You can also set one of the two parameters to
* as its default value, meaning that
it matches everything, meaning all status codes.
The above is an example where ?Subnet,
and ?StatusCode are used as
single-value parameters that is, you can input just one value for
those parameters.
Multi-value Parameters
You can use multivalued parameters to select more options from a list of available values:
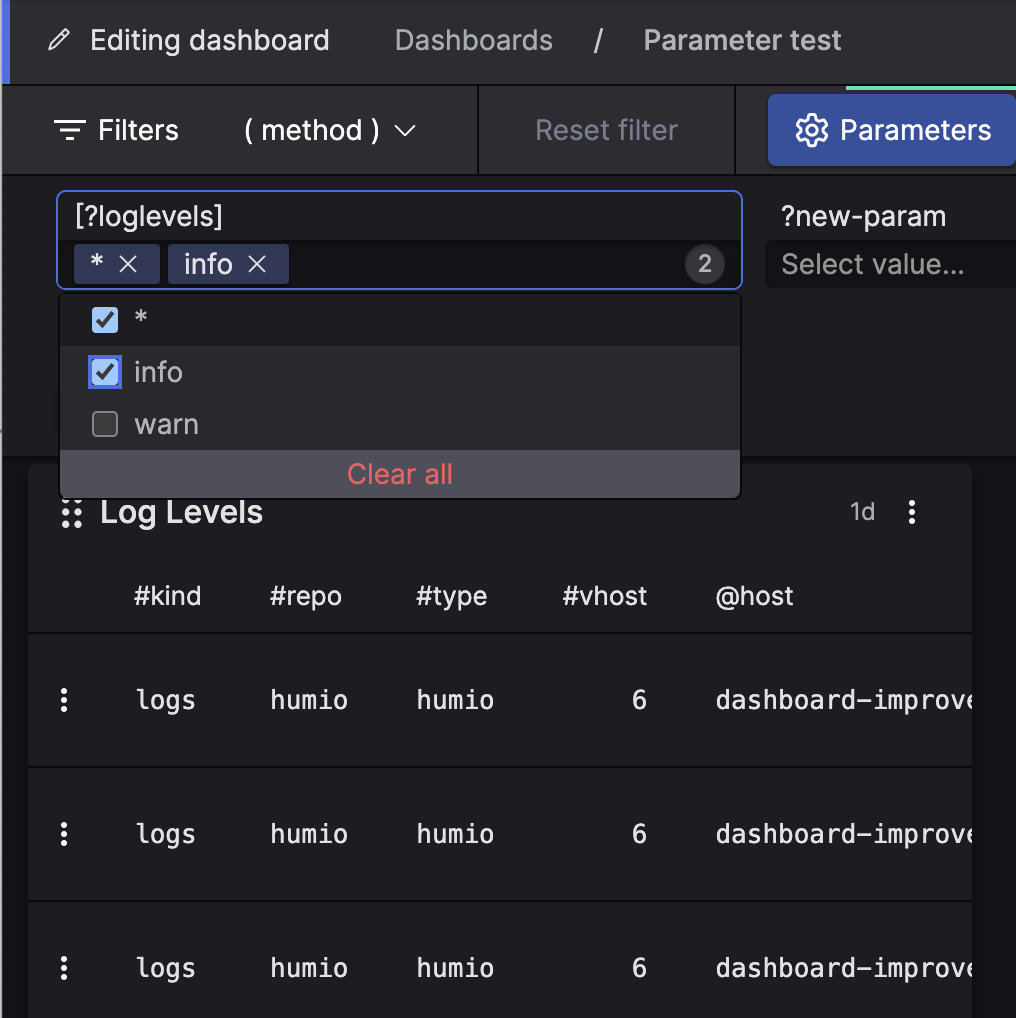 |
Figure 184. Multivalue Parameters Selection
Multiple values can be added at once to a multi-value parameter by using comma as a delimiter for the list of values, so that the values can be used individually. Syntax options for adding values to multi-value parameters are described at Multi-Value Dashboard Parameters Syntax.
Use the button to remove the selected values from the list in one click.
The example in figure above is produced from the query:
in(field=loglevel, values=[?loglevels])
A dashboard parameter of any
type automatically
becomes a multi-value parameter only when it appears inside brackets
([ ]) in all queries on that
dashboard. For example, the parameter
?loglevels in the query above is
inside brackets to indicate multi-value support, meaning it enables to
submit the values of the
loglevel field, such as
INFO and WARN.
If any query on the dashboard uses the same parameter without brackets, the parameter does not support multi-value functionality for that dashboard.
When the query is executed, the selected values are combined in the query into a comma-separated string. Using the same example, the query becomes:
in(field=loglevel, values=["INFO", "WARN"])As mentioned above, if the same parameter appears as both single-value and multi-value in two queries within a dashboard, the dashboard treats it as a single-value parameter for compatibility.
For example, consider a dashboard with two queries using the
?loglevel parameter. The first query
uses ?loglevel as a multi-value
parameter (inside brackets):
in(field=loglevel, values=[?loglevels])
The second query uses ?loglevel as a
single-value parameter (without brackets):
loglevel=?loglevel
| groupBy(loglevel)
Another example of query serving well for a multi-value parameter
would use the field method
with its values counted in a timeChart()
function:
in(method, values=[?method])
| timeChart()
With GET and POST
selected for the ?method parameter in
the Time Chart widget, the query will
be executed as:
in(method, values = ["GET", "POST"])
| timeChart(method)and will produce a visualization limited to the selected methods:
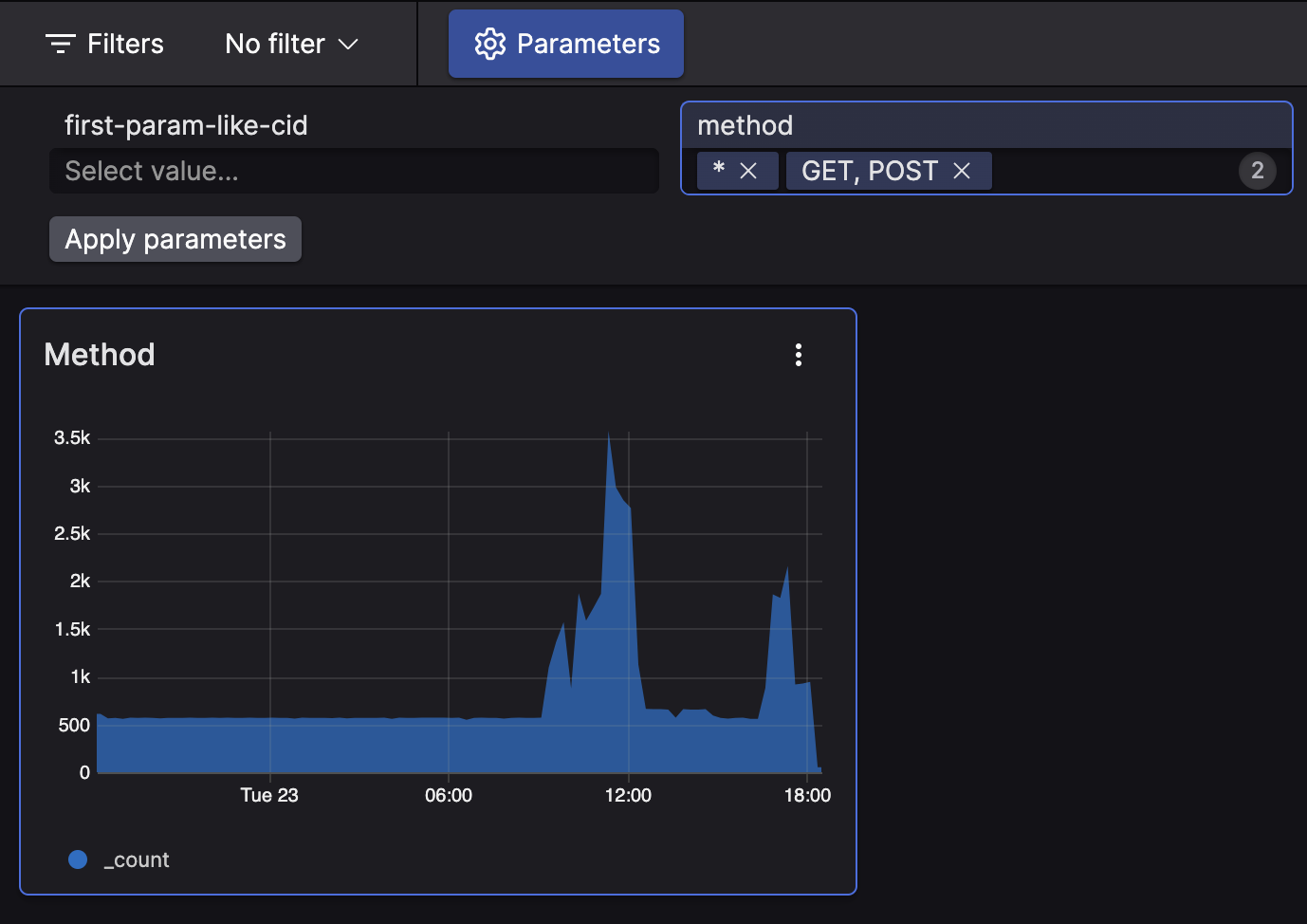 |
Figure 185. Widget with Multivalued Parameter in TimeChart
Parameters Referenced in Other Parameters
It is a common scenario to have multiple parameters, with one
parameter depending on another. For example, a dashboard used to see
how a specific host is doing may have a parameter which selects which
region or data center to look at
(?region parameter), and then a second
parameter to list the hosts available to choose from
(?host parameter).
In that scenario, the second parameter should naturally only show the hosts within the region you've selected previously.
You can reference other parameters if you are using either a Query Parameter or a File Parameter types. That is, all types of parameters can be referenced, but only query and file-based parameters can contain references.
For example, if the ?host parameter is
a query-based parameter, it might be populated by a query similar to:
groupBy(hostName, function=[])
in which case referencing the ?region
parameter becomes a matter of using that parameter in the query, same
as you would reference it in other queries:
hostRegion = ?region
| groupBy(hostName, function=[])
For file-based parameters, you can also reference another parameter
simply by referring to it. Say ?host
is a file-based parameter, based on a CSV file like this:
|-----------------------|
| regionName | hostName |
| us | host-1 |
| us | host-2 |
| eu | host-3 |
|-----------------------|
For this file-based parameter, you can add a value filter, which can
reference another parameter. In other words, you can specify that the
regionName column must match
what is selected in the ?region
parameter, as shown in the parameter configuration here depicted:
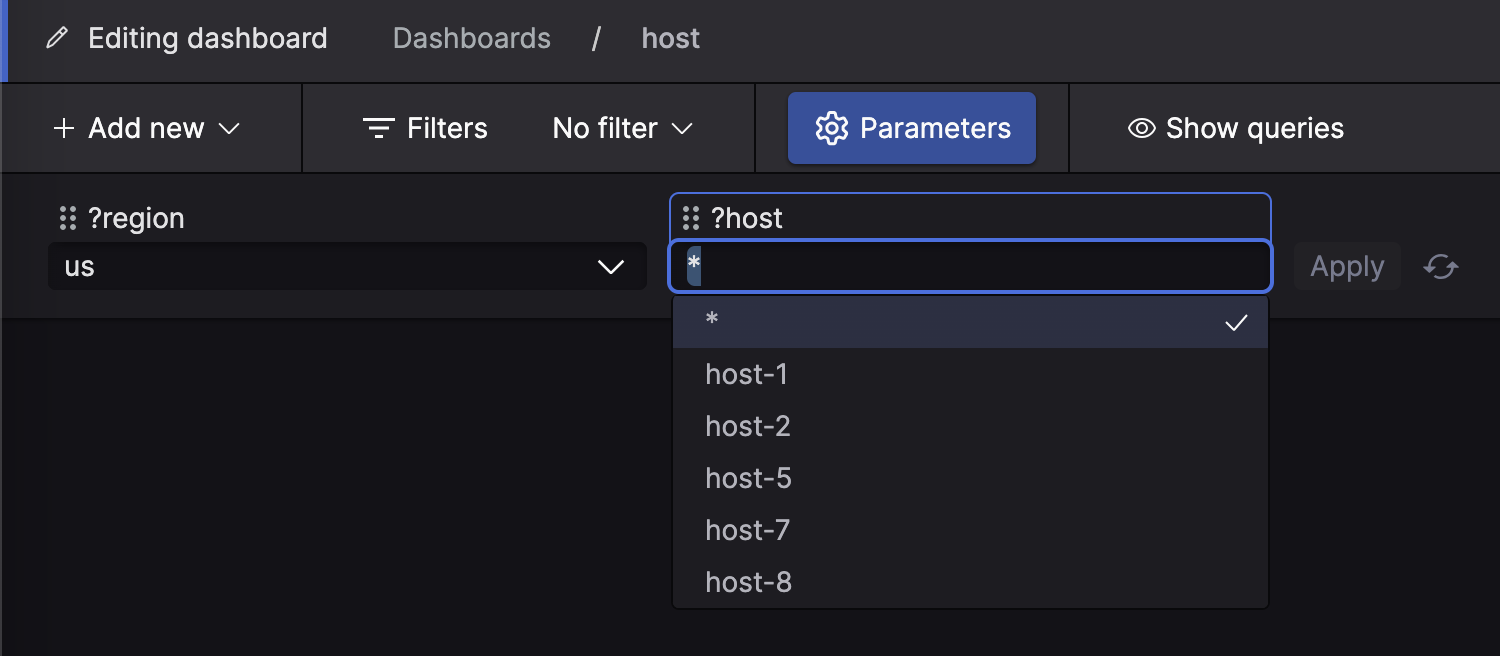 |
Figure 186. Multiple Parameters in a File Parameter
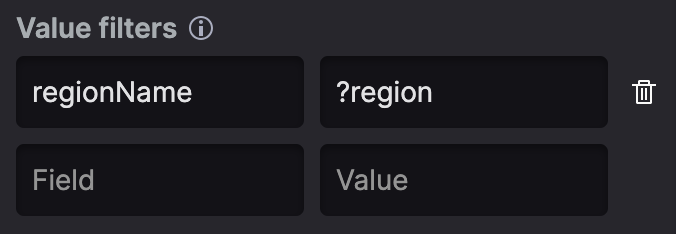 |
Figure 187. Referenced Parameter Configuration
Parameters with Regex
A parameter can only be assigned a fixed value, the value from a parameter cannot be used within a regex, for example:
/error="?error"/i
One way to work-around this is to use the parameter as the entire
regex to the regex() function:
regex(?regex, field="message")In the above example we use a parameter to represent the string used as a regular expression that is matched against the field message.
You also cannot provide an array:
["foo","bar"]Or a subquery
foo AND barParameters with Aggregate Query Functions
Usually you will want to fill in the
Query String field with a
LogScale query that uses an aggregate function like
top() and find the most frequent values that
appear in a certain field. For example, you could find all hosts in
your production cluster using:
env=PROD
| top(host)
You will need to then set host as the value in
Dropdown Value Field, meaning it is the
value of this field (host) in
the search results from the query env=PROD |
top(host) that should be bound to the parameters.
Using top() like in the example above is useful
to get the most frequent values. If instead you want all possible
values from the data, you can use the groupBy()
function to get those values.
The most efficient way to do so is by calling
groupBy() with no aggregation function, using:
groupBy(fieldName, function=[])
This will make groupBy() just gather the unique
values without doing any operations on those values (like counting how
many times they occur).
You can use the same parameter names in different queries for different widgets, so that the parameters shown in the dashboard will apply to any widget in that dashboard.
Parameters with Case-Insensitive Searches
Parameters can be used in case-insensitive searches; in the example
below the field Username is
filtered based on the inputUserName
parameter value:
| inputUserName := ?parameterUserName
| test(lower(inputUserName) == lower(UserName))