Lookup Files
Security Requirements and Controls
Data read accesspermission
Lookup files are used to add additional context to data, enabling you to attach or replace fields from events recorded in a repository when searched. Lookup files can also be used to filter data by calling the lookup file in a query function.
To add a lookup file, create or import a CSV (comma-separated value) or JSON
file and upload it to the repository or view.
An overview table allows for searching and
filtering to easily find and manage the available
files.The Lookup
files page allows for searching to easily find and manage
lookup files.
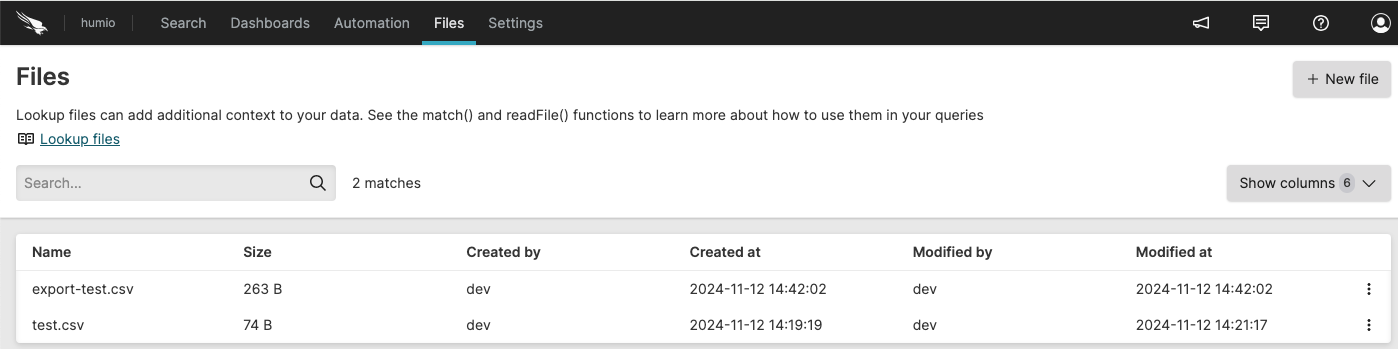 |
Figure 43. Files View
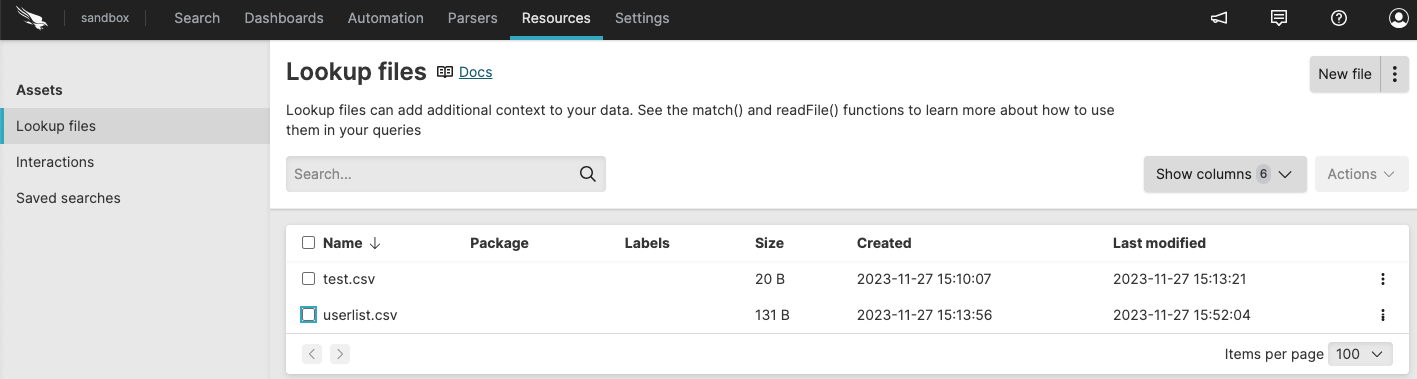 |
Figure 44. Lookup Files View
The files can be used together with query functions to provide lookups and
matching using the match() function.
The feature also works with the readFile() function for
reading a file which is used as data input for your query.
Once uploaded, files are synchronized across all the nodes within the cluster. Depending on the size of the file, and what queries may be being executed, there may be a delay before the updated file is available to queries.
The following operations are available:
For information on how Lookup files interact with the rest of the system, see Lookup files operations.
Supported file types and formats
LogScale supports two different file formats for uploaded lookup files: JSON and CSV.
| CSV Files | JSON Files | |
|---|---|---|
| Viewable within LogScale UI | Yes | No |
| Appendable within LogScale | Yes | No |
| Editable within LogScale UI | Yes | No |
| File Size Limit |
Variable default: MaxCsvFileUploadSizeBytes)
|
Variable default: MaxJsonFileUploadSizeBytes)
|
Each file format has some specific rules that are described in the section for each file format type. For both formats, the following apply:
Individual keys and values should be quoted, even as a number.
Important
Nested objects, that is an object within the returned object, are not supported. For example:
{
"1": { "name": "chr", "roles": { "user" : true }},
"2": { "name": "krab" },
"4": { "name": "pmm" },
"7": { "name": "mgr" }
}
would return only the simple field, name when used
with match(); the remainder of the embedded object
would be not be returned or included in the events. LogScale
does not reject files in this format.
Lookup files using CSV format
When using CSV for lookup files, the following rules apply:
Individual fields should be separated by a comma (
,)Whitespace is always included in the imported fields, the input takes the literal contents split by the comma character.
Fields can optionally be quoted by double quotes, for example to include commas in the imported values.
The first line of the CSV is interpreted as the column header and can be used as the field name when looking up values with functions like
match().
For example, the CSV file:
number,code,description
17,udp,UDP
80,http,HTTP Service
ip,"Internet Protocol, pseudo protocol"Would be interpreted as:
| number | code | description |
|---|---|---|
| 17 | udp | UDP |
| 80 | http | HTTP Service |
| ip | Internet Protocol, pseudo protocol |
CSV files can be viewed within the Lookup
files interface to confirm how the information has been
interpreted.
Lookup files using JSON format
When using JSON files, two different formats are supported: object-based and array-based.
JSON must be formatted in strict notation format. This requires no trailing commas (where there is no additional value),
Important
Once uploaded, JSON files cannot be viewed or updated. They can be exported to confirm the file format.
Object-based
In the object-based format, format the JSON as a hash or associative array, with a single key and corresponding object. For example:
json{ "1": { "name": "chr" }, "2": { "name": "krab" }, "4": { "name": "pmm" }, "7": { "name": "mgr" } }When performing a lookup,
match()will return the object (as an event with multiple fields), based on the matching key.Array-based
In the array-based format, format the JSON as an array of objects. In this model, the keys for each individual object become fields that can be matched when performing a lookup. For example, in the file:
json[ { "userid": "1", "name": "chr" }, { "userid": "2", "name": "krab" }, { "userid": "4", "name": "pmm" }, { "userid": "7", "name": "mgr" } ]The userid and name fields in the JSON object can be used to lookup and return other key/value pairs as event fields/values. For example, the fragment:
logscale Syntax... | match(file="long.json",field=codename,column="name")would return the userid field for objects within the lookup file array.
Create a lookup file
Security Requirements and Controls
Create Filespermission
The methods to create lookup files are:
Create a file in the Lookup files interface
You can create a new lookup file from the LogScale user interface, and then populate the content manually.
In the menu, click
Files→ .In the menu, click
Lookup files→ .Specify a name for the file in the New file dialog.
Click : this creates a new empty table.
Click to add rows and columns to your table and start fill it in as required.
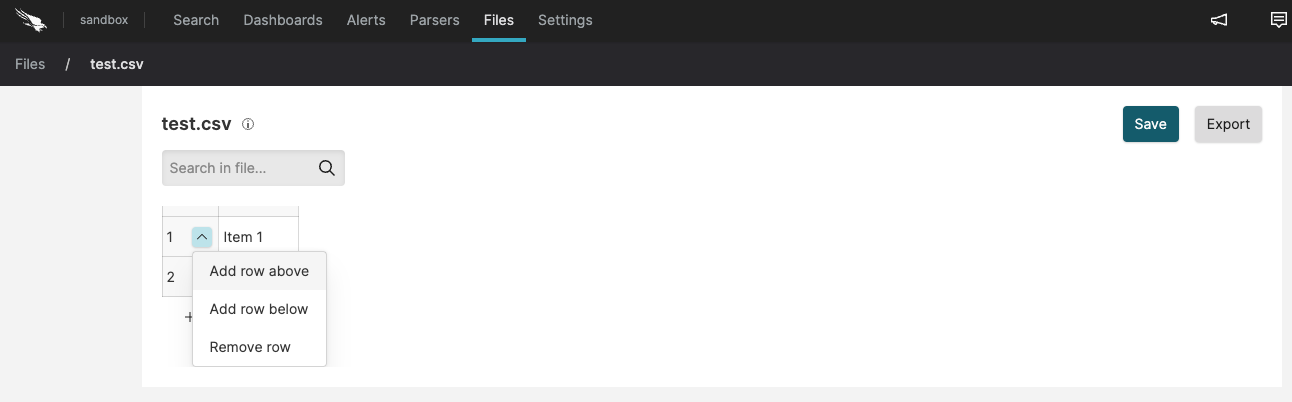
Figure 45. Create New CSV File
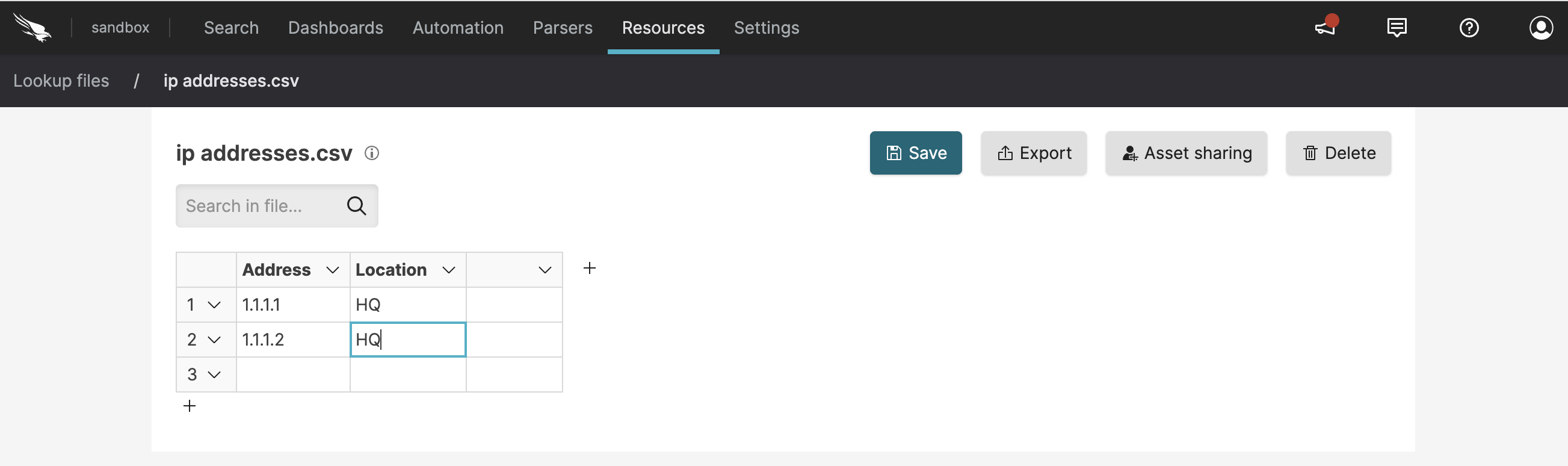
Figure 46. Create New CSV Lookup File
Click to save the changes.
If you have many changes to make, editing a data table through the
Files interface page can be tedious;
click and then
save the file to a location to edit the it in a spreadsheet program or a
simple text editor.
If you have many changes to make, editing a data table through the
Lookup files page can be tedious; click
and then save
the file to a location to edit the it in a spreadsheet program or a
simple text editor.
Note
Files larger than 100 MB cannot be viewed in the UI. Files with more than 1000 lines cannot be edited.
When a file is referenced in a query, a tab bearing the same name of the
file shows up in the Search page. This
file tab will display the file content as a
Table widget. Alternatively, if the file
cannot be queried, a download link will be presented instead. For
example, executing the query:
groupBy([status])
| match(file="status_codes.csv", column="code", field="status", include=name)groupBy([status])
| match(file="status_codes.csv", column="status", field=status, include=name)will show a new tab named Table: status_codes.csv:
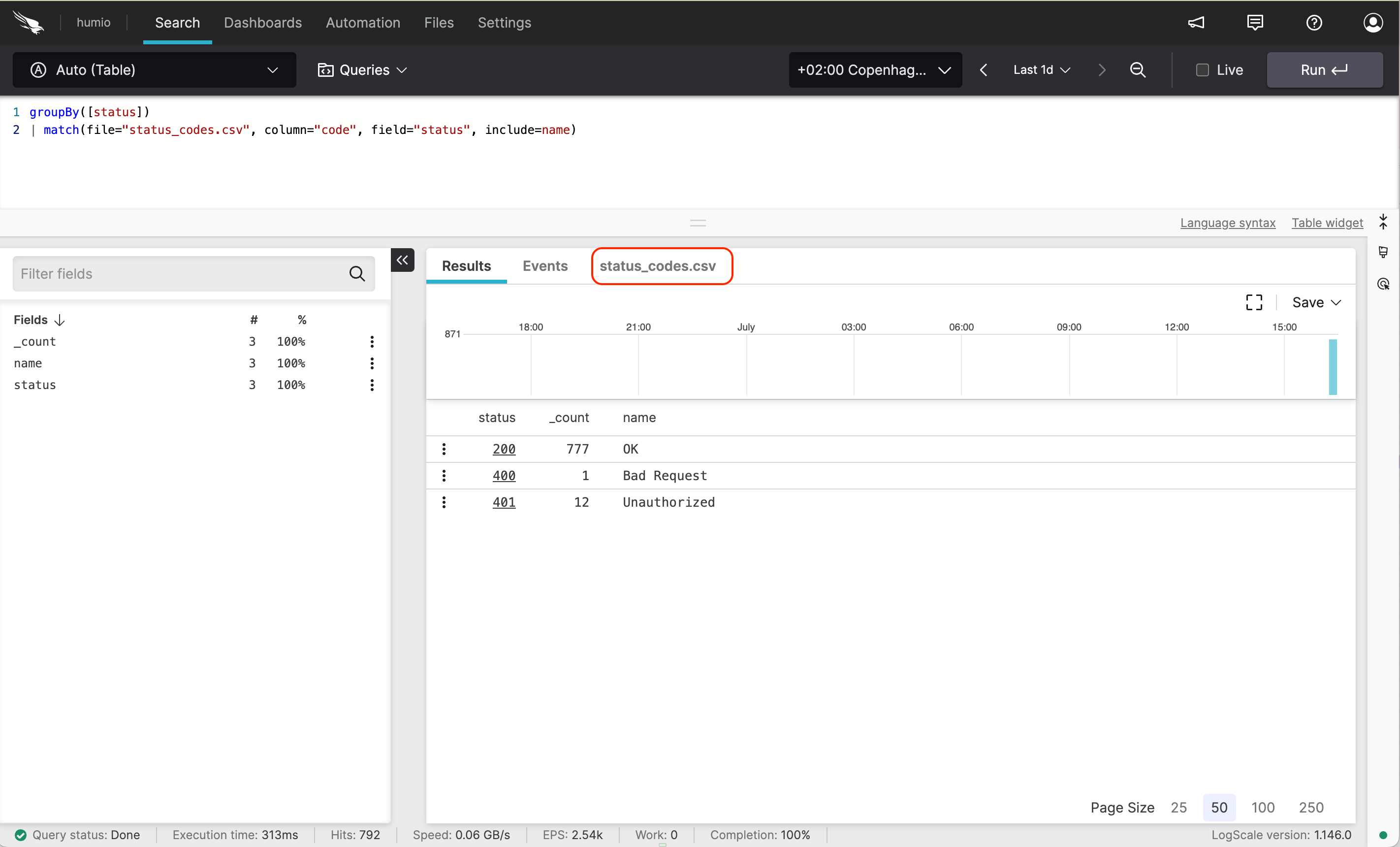 |
Figure 47. File Tab in Search View
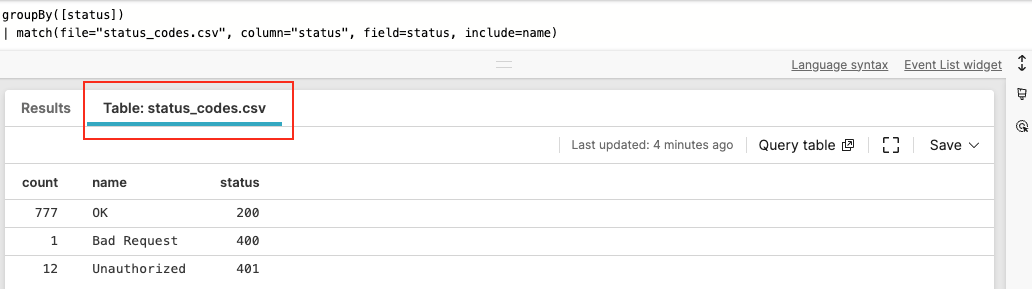 |
Figure 48. File Tab in Search View
Upload lookup files
Security Requirements and Controls
Create Filespermission
If you created or edited a lookup file in an external system, you can upload it to LogScale.
Click the menu → on the left navigation tree
Click the three dots next to → .
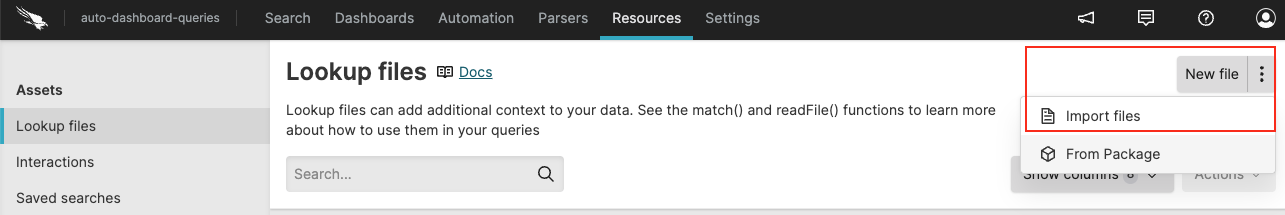
Figure 49. Import CSV File
Drag and drop your file or browse for the file to upload. You can import multiple files at once. Maximum allowed size is 209.72 MB.
You can upload a CSV file containing text like what you see below, which is essentially a lookup table that you can use for labels or value lookups.
csvuserid,ip,username,region 1,"212.12.31.23","pete","EU" 2,"212.12.31.231","bob","EU" 3,"98.12.31.21","anders","EU" 4,"121.12.31.23","jeff","US" 5,"82.12.31.23","ted","AU" 6,"62.12.31.23","annie","US" 7,"122.12.31.23","joe","CH" 8,"112.11.11.21","alice","CH" 9,"212.112.131.22","admin","RU" 10,"212.12.31.23","wendy","EU"Once it has been uploaded, it will look like what you see in Figure 50, “Import CSV File”.
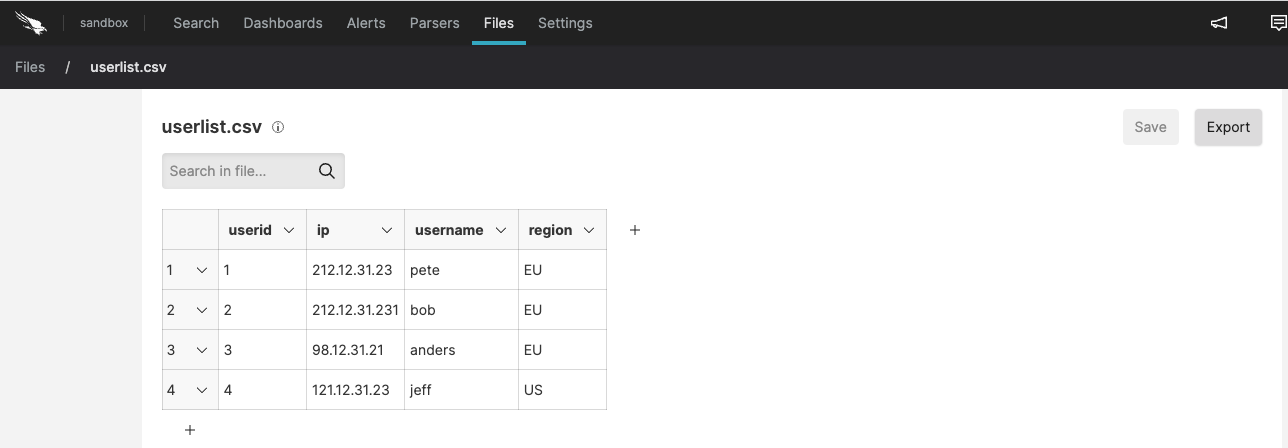
Figure 50. Import CSV File
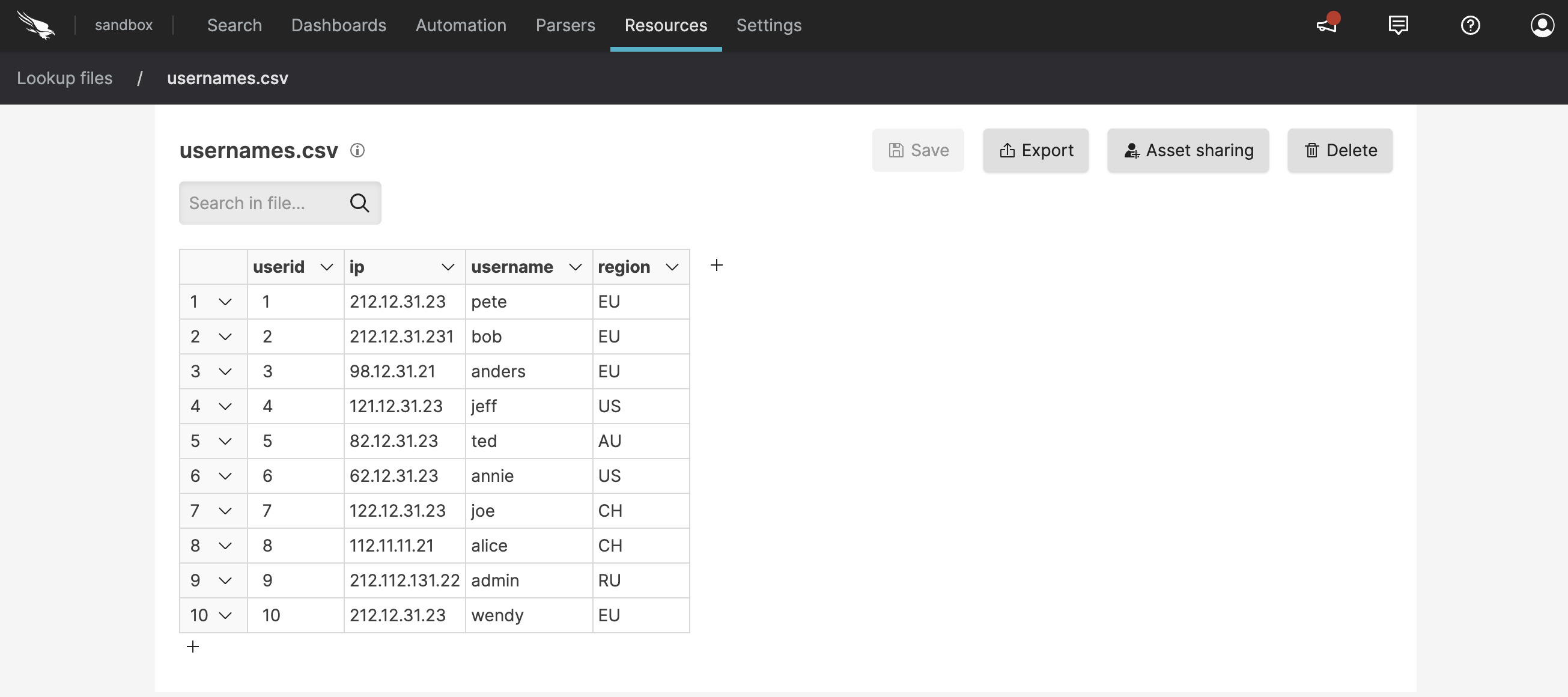
Figure 51. Import CSV File
Typically, the content is used within the
match()to lookup fixed reference information. Notice that the values are in quotes, except for the ones for userid, which are integers. See the Lookup API reference page for more information on this topic.Once created or uploaded, the file can be edited and updated within the user interface. Additional columns and rows can be added to the file using the button. Clicking the tiny information icon next to the file name displays metadata info about the file (created by, time it was created, etc.)
Important
Only CSV files can be edited once uploaded within the user interface.
Once you have finished editing, click , or click if you wish to download the edited file.
Create a lookup file through a trigger action
Security Requirements and Controls
Create ActionspermissionCreate FilespermissionUpdate Filespermission
It is possible to create and update a lookup file with an action connected to a trigger. This means that the first time the action triggers, a lookup file will be created. And then, the lookup file will be changed on subsequent action triggers.
For more information about how to create an action that creates a lookup file, see Action Type: Upload File.
Update lookup files
Security Requirements and Controls
Update Filespermission
Sometimes it's necessary to update the content of lookup files. If you are running a trigger with a lookup file action, you can configure the action to update the file automatically based on the results of the trigger.
If you are not updating the lookup file automatically with a trigger as described above, the following methods are available to update lookup files:
Go to the menu and select . Click on the file to update. Update the file as needed, adding or removing columns and rows, updating contents, and so on.
Update the lookup file externally and upload it to LogScale. To do this, export the lookup file and open it in another tool, make the necessary changes, and upload the file again.
Note
If you want the lookup file to be updated, appended, or overwritten by a query in a scheduled search, you must select the lookup file in an action attached to the scheduled search and choose the desired behavior when the query runs. For more information, see Action Type: Upload File.
Export lookup files
Security Requirements and Controls
Update Filespermission
You can export lookup files from LogScale as needed, for example, to augment content in third-party tools where it is easier to manipulate large amounts of data.
To export a file from the overview table, click the menu icon next to the file and select :
 |
Figure 52. Lookup file management actions
You can also export the lookup file when the file is open by clicking .
You can also export the lookup file when the file is open by clicking .
 |
Figure 53. Export file
Delete a lookup file
Security Requirements and Controls
Delete Filespermission
Warning
Deleting a file that is actively used by live queries will stop those queries.
To delete a file click the ⋮ menu icon next to the file.
 |
Figure 54. Lookup file management actions
You can also delete the lookup file when the file is open by clicking .
You can also export the lookup file when the file is open by clicking .
 |
Figure 55. Delete file
Permissions for files
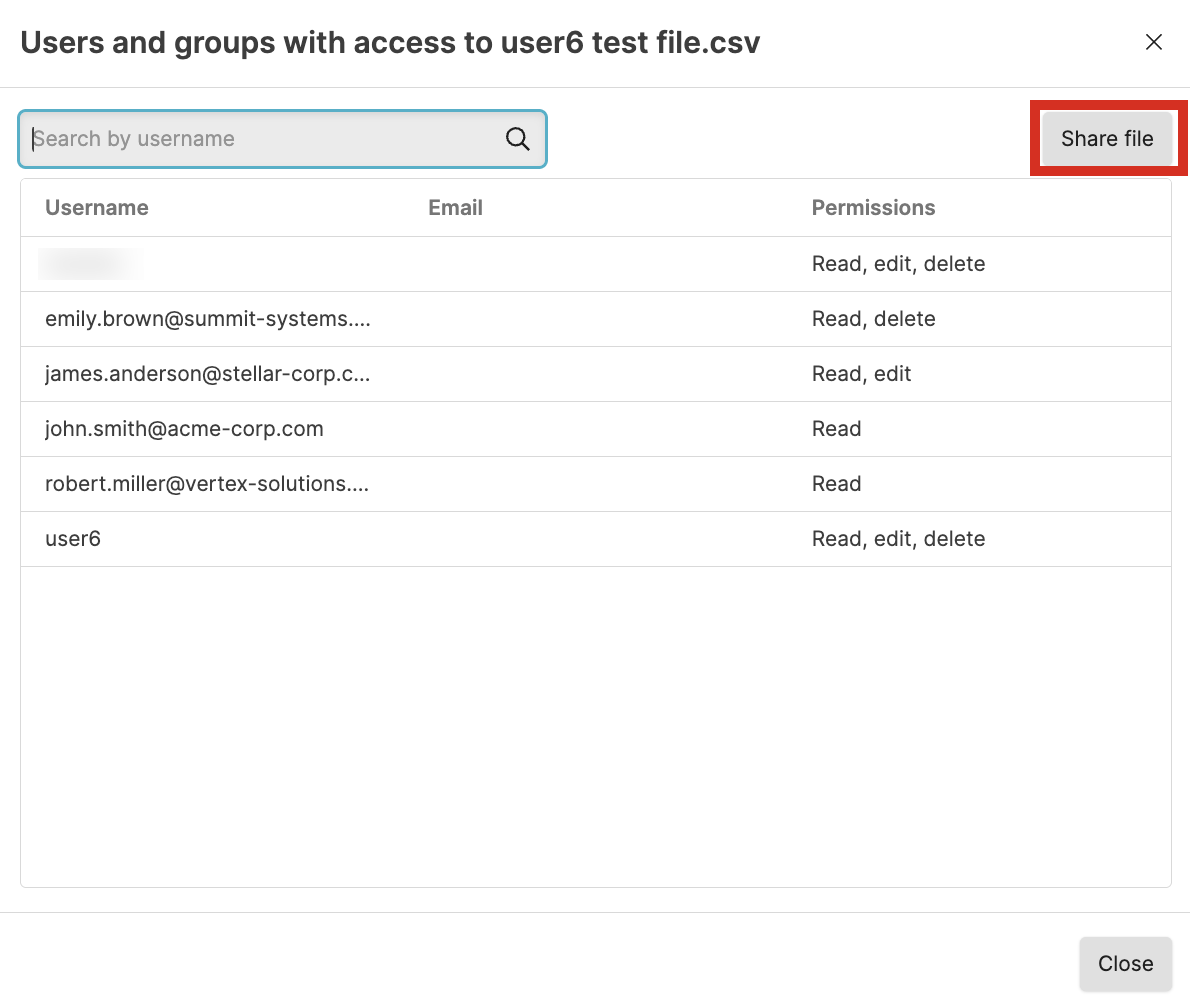
Security Requirements and Controls
Change user accesspermission
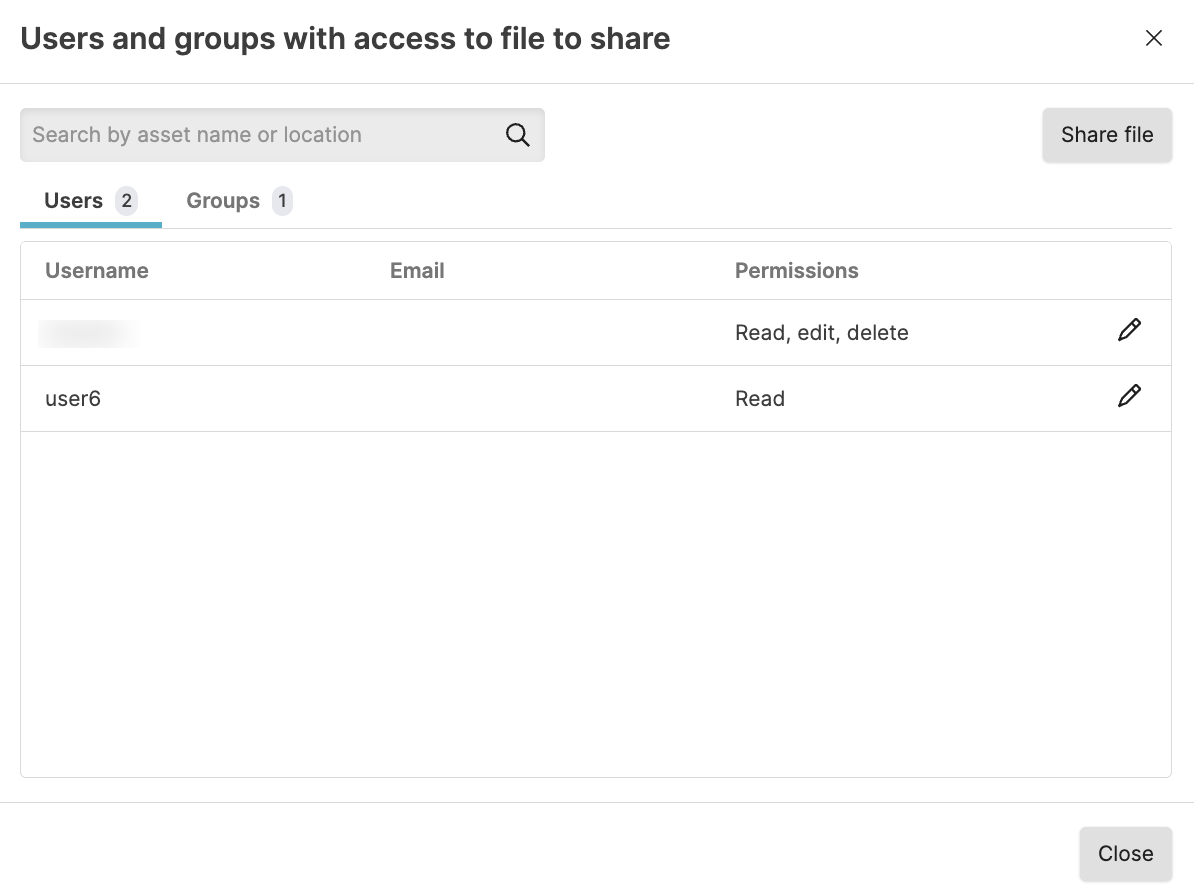
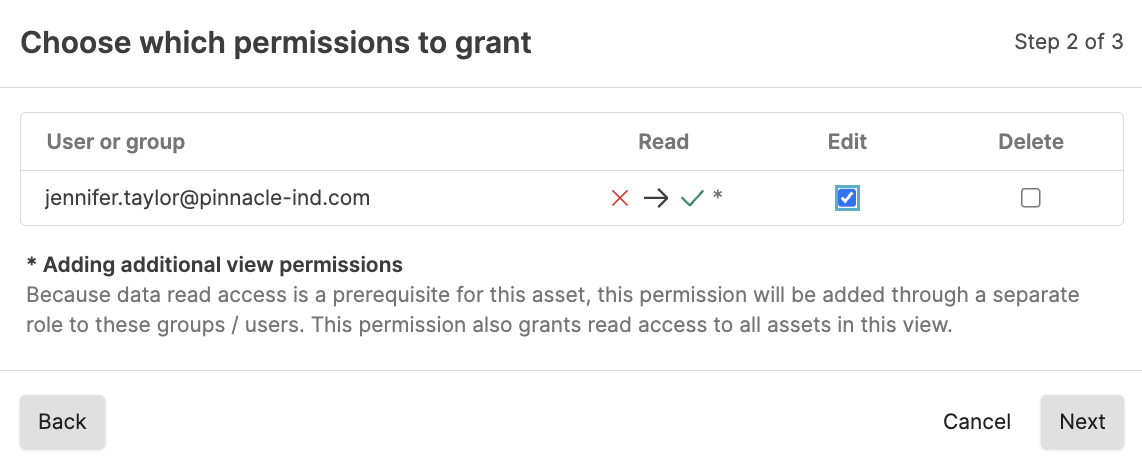
Sometimes you might want to collaborate with another user on a file, but that user does not have permission to files in the view. If you have permissions to do so, you can grant permissions to that user to edit and delete a particular file in a view. For more information about asset permissions, see Asset permissions.
If you do not have
Change user access
permission on the repository, you will see a list of users only (no
groups) that already have at least Read permissions on the repository. You
can select from these users and give them more permissions (up to the same
permissions you have).
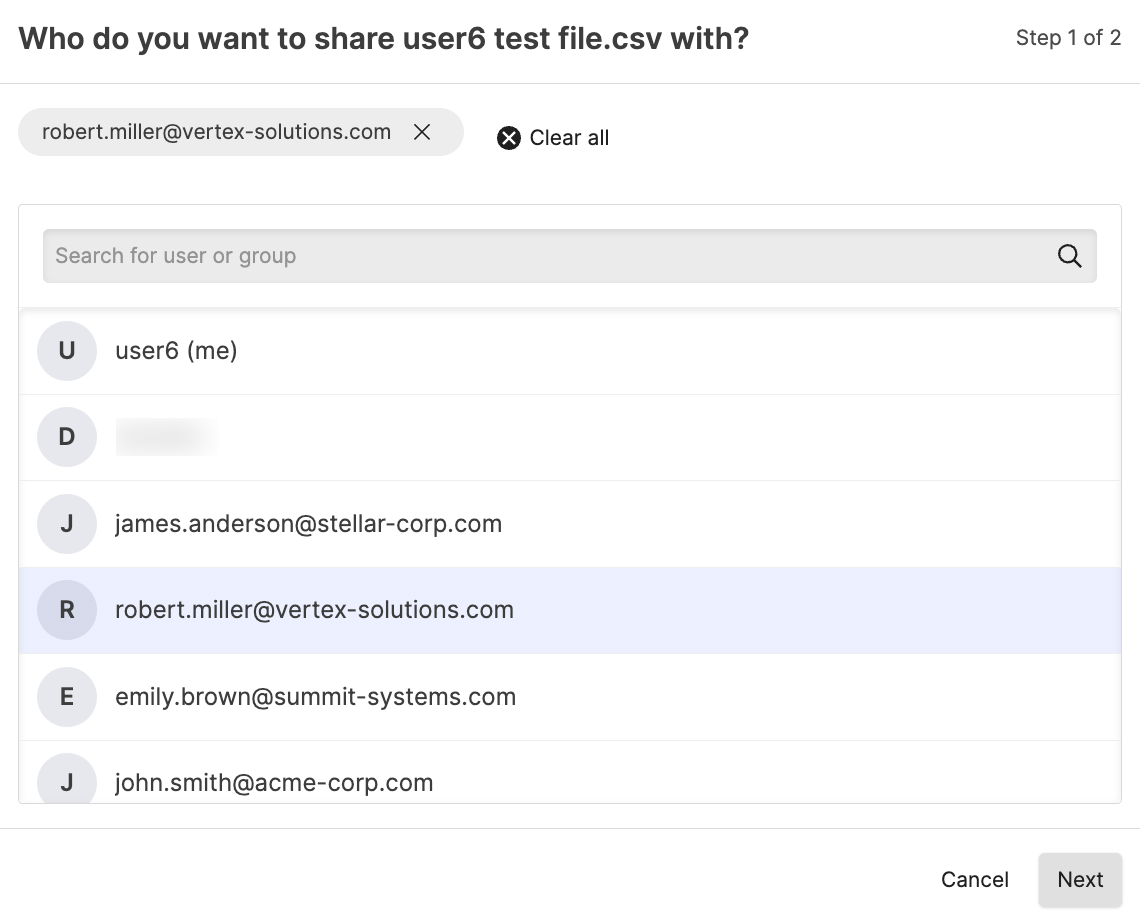
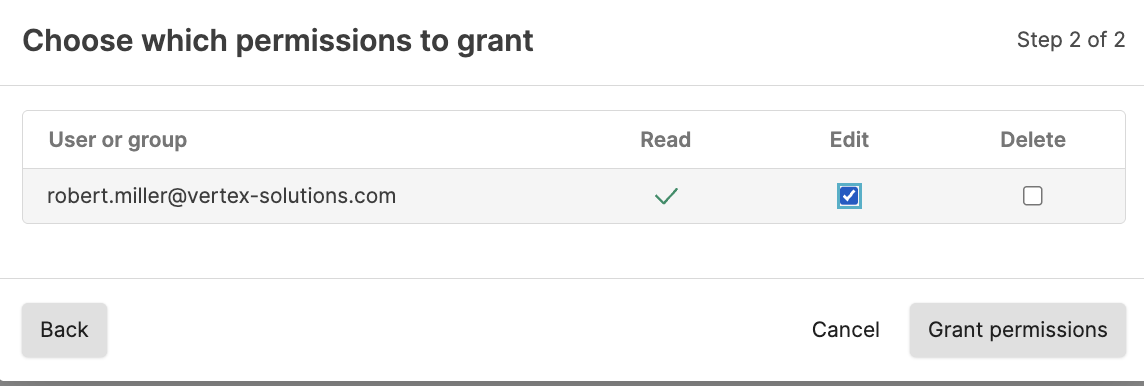
To grant access to edit or delete a file to another user or group:
Lookup files operations
When using Lookup files and match() functionality,
consider the following:
Lookup files use server memory proportional to the size of the file on disk, at least as much and typically more. If you have a 1Gb lookup file it will take up at least 1Gb of memory on some, potentially all, hosts within the cluster. This requirement should be taken into account when uploading and sizing the nodes within the cluster.
From LogScale v1.108 on, content of the file is shared among all queries that uses
match(), that is, the included columns that are common amongmatch()functions can be reused among queries.From 1.117 version on, whenever a file is updated, live queries and alert queries that use that file will seamlessly continue to run with the new updated file, thus making little difference if you have many small files to update or one large file. Since the file is swapped while the query is running, this also means that events can be queried with different versions of the file.
From LogScale v1.90, if you have large lookup files, wrap the uses of
match()in saved queries rather than use them directly across multiple different queries to ensure you don't accidentally pass slightly different argument in different queries. However, due to an improved reuse of files introduced in LogScale v1.108, this practice is no longer necessary starting from that version.