Cron Scheduling
Use the 'H' character in LogScale's scheduling interface to automatically distribute scheduled searches and reports to balance system load. This content covers UTC time specifications, minimum scheduling intervals for different operations, and important limitations around the template scheduling syntax.
A cron expression defines when your scheduled report or scheduled search runs using standard cron syntax:
* * * * *In order from left to right, the * in the example above represent:
Minute (0-59)
Hour (0-23, UTC by default)
Day of month (1-31)
Month (1-12)
Day of week (0-6, Sunday=0)
Special characters available:
* = any value
, = value list (e.g., 1,3,5)
- = range (e.g., 1-5)
/ = step values (e.g., */15 = every 15 minutes)
H = distributed hash (spreads load of scheduled search or scheduled report execution evenly). For information about using this for scheduled searches, see Using H for scheduled searches. For information about using this with scheduled reports, see Using H for scheduled reports.
So the following cron expression:
*/15 * * * *runs every 15 minutes.
Time specification is always based on UTC time, and not localized to the timezone where the server is located. To change the basis for the offset, set the UTC offset to the chosen time offset.
The smallest interval that can be configured for scheduled searches is one minute which can be configured by using:
* * * * *The smallest interval that can be configured for Schedule PDF Reports is one hour.
Be careful when using such small increments as this may increase the load on the cluster.
Using H for scheduled searches
Using H in the cron specification
allows LogScale to automatically choose the number of minutes past
each hour that a scheduled search will be run. This notation can be an
effective way to spread out the execution of scheduled searches without
having to monitor and track each scheduled search manually.
Instead of providing a fixed minute on which a scheduled search or
scheduled report should run, a template can be provided by specifying the
character H in the UI, which will
run a scheduled search at a random but fixed minute past the hour (based
on the hash of the ID).
When using H, the template will pick a number in the
range [0-59] for the minute when the
operation should run, and all consecutive operations will run on the same
minute. The operation will run at a fixed arbitrary minute past every
hour, meaning, for example, that if a search is made with the cron
expression schedule:
H * * * *and if the minute chosen is 48, the search will run at 00:48, 01:48, 02:48 etc.
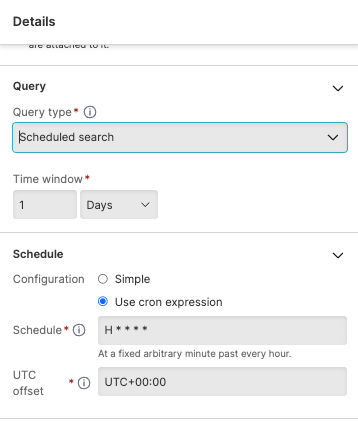 |
Figure 167. Cron Schedule with Template in a Scheduled Search
This method is only appropriate if you do not need to explicitly control
the search window. Because H automatically
chooses a minute, the search window will be determined by the chosen
figure. For example, if you use the H
notation to run the search from 24 hours ago to now, and the search runs
at 0:48, then the search window will be from 0:48 yesterday until 0:48
today.
Using H for scheduled reports
Using H in the cron specification
allows LogScale to automatically choose the number of minutes past
each hour that a scheduled report will be run. This notation can be an
effective way to spread out the execution of scheduled reports without
having to monitor and track each one manually.
When using H, the template will pick a number in the
range [0-59] for the minute when the
operation should run, and all consecutive operations will run on the same
minute. The operation will run at a fixed arbitrary minute past every
hour, meaning, for example, that if a search is made with the cron
expression schedule:
H * * * *
and if the minute chosen is 48, the search will run at 00:48, 01:48, 02:48
etc. This is only supported for minutes and only a lone
H is supported. The interval cannot be
controlled or modified, for example by using notation such as
H/15, or
H-15.